Ym1 induces RELMα and rescues IL-4Rα deficiency in lung repair during nematode infection
- PMID: 30500858
- PMCID: PMC6291165
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007423
Ym1 induces RELMα and rescues IL-4Rα deficiency in lung repair during nematode infection
Abstract
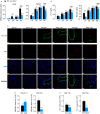
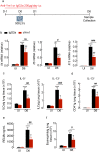
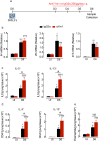
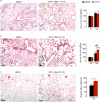
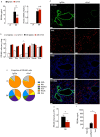
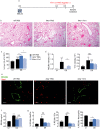
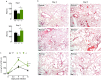
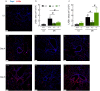
Ym1 and RELMα are established effector molecules closely synonymous with Th2-type inflammation and associated pathology. Here, we show that whilst largely dependent on IL-4Rα signaling during a type 2 response, Ym1 and RELMα also have IL-4Rα-independent expression patterns in the lung. Notably, we found that Ym1 has opposing effects on type 2 immunity during nematode infection depending on whether it is expressed at the time of innate or adaptive responses. During the lung migratory stage of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis, Ym1 promoted the subsequent reparative type 2 response but once that response was established, IL-4Rα-dependent Ym1 was important for limiting the magnitude of type 2 cytokine production from both CD4+ T cells and innate lymphoid cells in the lung. Importantly, our study demonstrates that delivery of Ym1 to IL-4Rα deficient animals drives RELMα production and overcomes lung repair deficits in mice deficient in type 2 immunity. Together, Ym1 and RELMα, exhibit time and dose-dependent interactions that determines the outcome of lung repair during nematode infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist and that no author has a financial or non-financial professional or personal relationship with GlaxoSmithKlein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transfer of in vivo primed transgenic T cells supports allergic lung inflammation and FIZZ1 and Ym1 production in an IL-4Rα and STAT6 dependent manner.BMC Immunol. 2011 Oct 20;12:60. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-12-60. BMC Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22014099 Free PMC article.
-
Chitinase and Fizz family members are a generalized feature of nematode infection with selective upregulation of Ym1 and Fizz1 by antigen-presenting cells.Infect Immun. 2005 Jan;73(1):385-94. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.1.385-394.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15618176 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of RELMα and RELMβ Single- and Double-Gene-Deficient Mice Reveals that RELMα Expression Dictates Inflammation and Worm Expulsion in Hookworm Infection.Infect Immun. 2016 Mar 24;84(4):1100-1111. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01479-15. Print 2016 Apr. Infect Immun. 2016. PMID: 26831469 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immune responses to lung-stage helminth infection induce alternatively activated alveolar macrophages.Infect Immun. 2006 Sep;74(9):4970-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00687-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16926388 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-4- and interleukin-13-mediated host protection against intestinal nematode parasites.Immunol Rev. 2004 Oct;201:139-55. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00192.x. Immunol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15361238 Review.
Cited by
-
Irreversible evolutionary loss of chitin-degrading ability in the chitinase-like protein Ym1 under positive selection in rodents.Protein Sci. 2023 Apr;32(4):e4620. doi: 10.1002/pro.4620. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 36883357 Free PMC article.
-
Th2-dependent STAT6-regulated genes in intestinal epithelial cells mediate larval trapping during secondary Heligmosomoides polygyrus bakeri infection.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Apr 5;19(4):e1011296. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011296. eCollection 2023 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37018382 Free PMC article.
-
Host Immunity and Inflammation to Pulmonary Helminth Infections.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 20;11:594520. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.594520. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33193446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Hypoxia-Induced Mitogenic Factor in Organ-Specific Inflammation in the Lung and Liver: Key Concepts and Gaps in Knowledge Regarding Molecular Mechanisms of Acute or Immune-Mediated Liver Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 8;22(5):2717. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052717. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33800244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabinoid Receptor Subtype-1 Regulates Allergic Airway Eosinophilia During Lung Helminth Infection.Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021 Jun;6(3):242-252. doi: 10.1089/can.2020.0167. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021. PMID: 33998896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen JE, Sutherland TE. Host protective roles of type 2 immunity: parasite killing and tissue repair, flip sides of the same coin. Semin Immunol. 2014;26: 329–340. 10.1016/j.smim.2014.06.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lawrence RA, Gray CA, Osborne J, Maizels RM. Nippostrongylus brasiliensis: cytokine responses and nematode expulsion in normal and IL-4-deficient mice. Exp Parasitol. 1996;84: 65–73. 10.1006/expr.1996.0090 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barner M, Mohrs M, Brombacher F, Kopf M. Differences between IL-4R alpha-deficient and IL-4-deficient mice reveal a role for IL-13 in the regulation of Th2 responses. Curr Biol. 1998;8: 669–672. - PubMed
-
- Chen F, Liu Z, Wu W, Rozo C, Bowdridge S, Millman A, et al. An essential role for TH2-type responses in limiting acute tissue damage during experimental helminth infection. 2012;18: 260–266. 10.1038/nm.2628 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Raes G, De Baetselier P, Noël W, Beschin A, Brombacher F, Hassanzadeh Gh G. Differential expression of FIZZ1 and Ym1 in alternatively versus classically activated macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 2002;71: 597–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

