OXA2b is Crucial for Proper Membrane Insertion of COX2 during Biogenesis of Complex IV in Plant Mitochondria
- PMID: 30487140
- PMCID: PMC6426407
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.18.01286
OXA2b is Crucial for Proper Membrane Insertion of COX2 during Biogenesis of Complex IV in Plant Mitochondria
Abstract
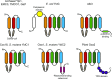
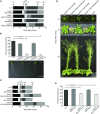
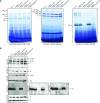
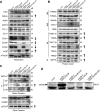
The evolutionarily conserved YidC/Oxa1/Alb3 proteins are involved in the insertion of membrane proteins in all domains of life. In plant mitochondria, individual knockouts of OXA1a, OXA2a, and OXA2b are embryo-lethal. In contrast to other members of the protein family, OXA2a and OXA2b contain a tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domain at the C-terminus. Here, the role of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) OXA2b was determined by using viable mutant plants that were generated by complementing homozygous lethal OXA2b T-DNA insertional mutants with a C-terminally truncated OXA2b lacking the TPR domain. The truncated-OXA2b-complemented plants displayed severe growth retardation due to a strong reduction in the steady-state abundance and enzyme activity of the mitochondrial respiratory chain complex IV. The TPR domain of OXA2b directly interacts with cytochrome c oxidase subunit 2, aiding in efficient membrane insertion and translocation of its C-terminus. Thus, OXA2b is crucial for the biogenesis of complex IV in plant mitochondria.
© 2019 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The OXA2a Insertase of Arabidopsis Is Required for Cytochrome c Maturation.Plant Physiol. 2020 Oct;184(2):1042-1055. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.01248. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Plant Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32759271 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis thaliana Oxa proteins locate to mitochondria and fulfill essential roles during embryo development.Planta. 2013 Feb;237(2):573-88. doi: 10.1007/s00425-012-1793-9. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Planta. 2013. PMID: 23179441
-
The Oxa2 protein of Neurospora crassa plays a critical role in the biogenesis of cytochrome oxidase and defines a ubiquitous subbranch of the Oxa1/YidC/Alb3 protein family.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Apr;15(4):1853-61. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-11-0789. Epub 2004 Feb 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 14767059 Free PMC article.
-
Oxa1/Alb3/YidC system for insertion of membrane proteins in mitochondria, chloroplasts and bacteria (review).Mol Membr Biol. 2005 Jan-Apr;22(1-2):101-11. doi: 10.1080/09687860500041718. Mol Membr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16092528 Review.
-
Inserting membrane proteins: the YidC/Oxa1/Alb3 machinery in bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Mar;1808(3):866-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2010.08.014. Epub 2010 Aug 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 20800571 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic markers and tree properties predicting wood biorefining potential in aspen (Populus tremula) bioenergy feedstock.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2023 Apr 10;16(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13068-023-02315-1. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2023. PMID: 37038157 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of new rice germplasms with low amylose content by CRISPR/CAS9-targeted mutagenesis of the FLOURY ENDOSPERM 2 gene.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Mar 13;14:1138523. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1138523. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36993856 Free PMC article.
-
The biogenesis and regulation of the plant oxidative phosphorylation system.Plant Physiol. 2023 May 31;192(2):728-747. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiad108. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36806687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental approaches to studying translation in plant semi-autonomous organelles.J Exp Bot. 2024 Sep 11;75(17):5175-5187. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae151. J Exp Bot. 2024. PMID: 38592734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemistry of Copper Site Assembly in Heme-Copper Oxidases: A Theme with Variations.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 5;20(15):3830. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153830. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31387303 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215: 403–410 - PubMed
-
- Benz M, Soll J, Ankele E (2013) Arabidopsis thaliana Oxa proteins locate to mitochondria and fulfill essential roles during embryo development. Planta 237: 573–588 - PubMed
-
- Blatch GL, Lässle M (1999) The tetratricopeptide repeat: A structural motif mediating protein-protein interactions. BioEssays 21: 932–939 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

