BICD1 mediates HIF1α nuclear translocation in mesenchymal stem cells during hypoxia adaptation
- PMID: 30464225
- PMCID: PMC6748134
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-018-0241-1
BICD1 mediates HIF1α nuclear translocation in mesenchymal stem cells during hypoxia adaptation
Abstract
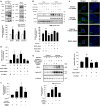
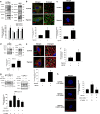
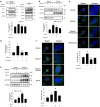
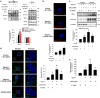
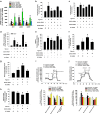
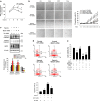
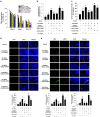
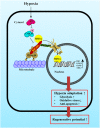
Hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF1α) is a master regulator leading to metabolic adaptation, an essential physiological process to maintain the survival of stem cells under hypoxia. However, it is poorly understood how HIF1α translocates into the nucleus in stem cells under hypoxia. Here, we investigated the role of a motor adaptor protein Bicaudal D homolog 1 (BICD1) in dynein-mediated HIF1α nuclear translocation and the effect of BICD1 regulation on hypoxia adaptation and its therapeutic potential on human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UCB-MSCs). In our results, silencing of BICD1 but not BICD2 abolished HIF1α nuclear translocation and its activity. BICD1 overexpression further enhanced hypoxia-induced HIF1α nuclear translocation. Hypoxia stimulated direct bindings of HIF1α to BICD1 and the intermediate chain of dynein (Dynein IC), which was abolished by BICD1 silencing. Akt inhibition reduced the binding of BICD1 to HIF1α and nuclear translocation of HIF1α. Conversely, Akt activation or GSK3β silencing further enhanced the hypoxia-induced HIF1α nuclear translocation. Furthermore, BICD1 silencing abolished hypoxia-induced glycolytic reprogramming and increased mitochondrial ROS accumulation and apoptosis in UCB-MSCs under hypoxia. In the mouse skin wound healing model, the transplanted cell survival and skin wound healing capacities of hypoxia-pretreated UCB-MSCs were reduced by BICD1 silencing and further increased by GSK3β silencing. In conclusion, we demonstrated that BICD1-induced HIF1α nuclear translocation is critical for hypoxia adaptation, which determines the regenerative potential of UCB-MSCs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
O-cyclic phytosphingosine-1-phosphate stimulates HIF1α-dependent glycolytic reprogramming to enhance the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Aug 5;10(8):590. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1823-7. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31383843 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Microtubule-Associated Factors in HIF1α Nuclear Translocation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1232:271-276. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34461-0_34. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31893420 Review.
-
PBX homeobox 1 enhances hair follicle mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and reprogramming through activation of the AKT/glycogen synthase kinase signaling pathway and suppression of apoptosis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Aug 23;10(1):268. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1382-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31443676 Free PMC article.
-
BNIP3 induction by hypoxia stimulates FASN-dependent free fatty acid production enhancing therapeutic potential of umbilical cord blood-derived human mesenchymal stem cells.Redox Biol. 2017 Oct;13:426-443. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Jul 4. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 28704726 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Roles of the Bicaudal D Family of Motor Adaptors.Vitam Horm. 2017;104:133-152. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Dec 29. Vitam Horm. 2017. PMID: 28215293 Review.
Cited by
-
The interplay between the tumor microenvironment and tumor-derived small extracellular vesicles in cancer development and therapeutic response.Cancer Biol Ther. 2024 Dec 31;25(1):2356831. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2356831. Epub 2024 May 20. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38767879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin activates ABCA1 via the BiP/NRF1 pathway to suppress high-cholesterol-induced apoptosis of mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Feb 5;12(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02181-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33546749 Free PMC article.
-
O-cyclic phytosphingosine-1-phosphate stimulates HIF1α-dependent glycolytic reprogramming to enhance the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Aug 5;10(8):590. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1823-7. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31383843 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of hypoxia-inducible genes is suppressed in altered gravity due to impaired nuclear HIF1α accumulation.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 4;13(1):14514. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41686-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37666879 Free PMC article.
-
Ephedrine attenuates LPS-induced M1 polarization of alveolar macrophages via the PKM2-mediated glycolysis.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Oct 10;13(5):tfae166. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae166. eCollection 2024 Oct. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39399212
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

