Mass Action Kinetic Model of Apoptosis by TRAIL-Functionalized Leukocytes
- PMID: 30460191
- PMCID: PMC6232872
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00410
Mass Action Kinetic Model of Apoptosis by TRAIL-Functionalized Leukocytes
Abstract
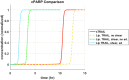
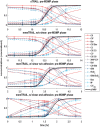
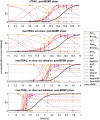
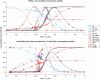
Background: Metastasis through the bloodstream contributes to poor prognosis in many types of cancer. A unique approach to target and kill colon, prostate, and other epithelial-type cancer cells in the blood has been recently developed that uses circulating leukocytes to present the cancer-specific, liposome-bound Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) on their surface along with E - selectin adhesion receptors. This approach, demonstrated both in vitro with human blood and in mice, mimics the cytotoxic activity of natural killer cells. The resulting liposomal TRAIL-coated leukocytes hold promise as an effective means to neutralize circulating tumor cells that enter the bloodstream with the potential to form new metastases. Methods: The computational biology study reported here examines the mechanism of this effective signal delivery, by considering the kinetics of the coupled reaction cascade, from TRAIL binding death receptor to eventual apoptosis. In this study, a collision of bound TRAIL with circulating tumor cells (CTCs) is considered and compared to a prolonged exposure of CTCs to soluble TRAIL. An existing computational model of soluble TRAIL treatment was modified to represent the kinetics from a diffusion-limited 3D reference frame into a 2D collision frame with advection and adhesion to mimic the E - selectin and membrane bound TRAIL treatment. Thus, the current model recreates the new approach of targeting cancer cells within the blood. The model was found to faithfully reproduce representative observations from experiments of liposomal TRAIL treatment under shear. Results: The model predicts apoptosis of CTCs within 2 h when treated with membrane bound TRAIL, while apoptosis in CTCs treated with soluble TRAIL proceeds much more slowly over the course of 10 h, consistent with previous experiments. Given the clearance rate of soluble TRAIL in vivo, this model predicts that the soluble TRAIL method would be rendered ineffective, as found in previous experiments. Conclusion: This study therefore indicates that the kinetics of the coupled reaction cascade of liposomal E - selectin and membrane bound TRAIL colliding with CTCs can explain why this new approach to target and kill cancer cells in blood is much more effective than its soluble counterpart.
Keywords: TRAIL; apoptosis; cancer; circulating tumor cells (CTC); modeling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TRAIL-coated leukocytes that kill cancer cells in the circulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 21;111(3):930-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1316312111. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24395803 Free PMC article.
-
Unnatural killer cells to prevent bloodborne metastasis: inspiration from biology and engineering.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2014 Jun;14(6):641-4. doi: 10.1586/14737140.2014.916619. Epub 2014 May 5. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24791860 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of apoptotic signal to rolling cancer cells: a novel biomimetic technique using immobilized TRAIL and E-selectin.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2009 Apr 15;102(6):1692-702. doi: 10.1002/bit.22204. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2009. PMID: 19073014
-
TRAIL-NP hybrids for cancer therapy: a review.Nanoscale. 2017 May 11;9(18):5755-5768. doi: 10.1039/c7nr01469d. Nanoscale. 2017. PMID: 28443893 Review.
-
Should We Keep Walking along the Trail for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment? Revisiting TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand for Anticancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Mar 18;10(3):77. doi: 10.3390/cancers10030077. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29562636 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of Piezo1 sensitizes cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis through mitochondrial outer membrane permeability.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Nov 4;10(11):837. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2063-6. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31685811 Free PMC article.
-
TRAIL receptor-induced features of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition increase tumour phenotypic heterogeneity: potential cell survival mechanisms.Br J Cancer. 2021 Jan;124(1):91-101. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-01177-w. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Br J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33257838 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

