DNA Vaccines-How Far From Clinical Use?
- PMID: 30445702
- PMCID: PMC6274812
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19113605
DNA Vaccines-How Far From Clinical Use?
Abstract
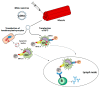
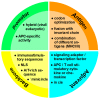
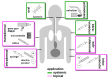
Two decades ago successful transfection of antigen presenting cells (APC) in vivo was demonstrated which resulted in the induction of primary adaptive immune responses. Due to the good biocompatibility of plasmid DNA, their cost-efficient production and long shelf life, many researchers aimed to develop DNA vaccine-based immunotherapeutic strategies for treatment of infections and cancer, but also autoimmune diseases and allergies. This review aims to summarize our current knowledge on the course of action of DNA vaccines, and which factors are responsible for the poor immunogenicity in human so far. Important optimization steps that improve DNA transfection efficiency comprise the introduction of DNA-complexing nano-carriers aimed to prevent extracellular DNA degradation, enabling APC targeting, and enhanced endo/lysosomal escape of DNA. Attachment of virus-derived nuclear localization sequences facilitates nuclear entry of DNA. Improvements in DNA vaccine design include the use of APC-specific promotors for transcriptional targeting, the arrangement of multiple antigen sequences, the co-delivery of molecular adjuvants to prevent tolerance induction, and strategies to circumvent potential inhibitory effects of the vector backbone. Successful clinical use of DNA vaccines may require combined employment of all of these parameters, and combination treatment with additional drugs.
Keywords: DNA vaccine; adjuvant; antigen presenting cells; dendritic cell; macrophage; nano carrier; promotor; transgene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced non-inflammasome mediated immune responses by mannosylated zwitterionic-based cationic liposomes for HIV DNA vaccines.Biomaterials. 2016 Apr;85:1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.01.054. Epub 2016 Jan 29. Biomaterials. 2016. PMID: 26851653
-
APC targeted micelle for enhanced intradermal delivery of hepatitis B DNA vaccine.J Control Release. 2015 Jun 10;207:143-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.04.014. Epub 2015 Apr 14. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 25886704
-
Molecular mechanisms for enhanced DNA vaccine immunogenicity.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2016;15(3):313-29. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2016.1124762. Epub 2015 Dec 28. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2016. PMID: 26707950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adjuvants may reduce in vivo transfection levels for DNA vaccination in mice leading to reduced antigen-specific CD8+ T cell responses.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(9):2305-11. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1047567. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015. PMID: 26091088 Free PMC article.
-
DNA vaccination: antigen presentation and the induction of immunity.J Leukoc Biol. 2000 Dec;68(6):793-806. J Leukoc Biol. 2000. PMID: 11129646 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a DNA Vaccine for Melanoma Metastasis by Inhalation Based on an Analysis of Transgene Expression Characteristics of Naked pDNA and a Ternary Complex in Mouse Lung Tissues.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Jun 11;12(6):540. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12060540. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32545209 Free PMC article.
-
Human lung-on-chips: Advanced systems for respiratory virus models and assessment of immune response.Biomicrofluidics. 2021 Mar 23;15(2):021501. doi: 10.1063/5.0038924. eCollection 2021 Mar. Biomicrofluidics. 2021. PMID: 33791050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of the Reverse Transcriptase Domain of Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Induces Lytic Cellular Response in DNA-Immunized Mice and Limits Tumorigenic and Metastatic Potential of Murine Adenocarcinoma 4T1 Cells.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Jun 18;8(2):318. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8020318. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32570805 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Vaccines: Their Formulations, Engineering and Delivery.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Jan 11;12(1):71. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12010071. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38250884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-Assembled Particles Combining SARS-CoV-2 RBD Protein and RBD DNA Vaccine Induce Synergistic Enhancement of the Humoral Response in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 16;23(4):2188. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042188. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216301 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

