The RecB helicase-nuclease tether mediates Chi hotspot control of RecBCD enzyme
- PMID: 30445486
- PMCID: PMC6326792
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky1132
The RecB helicase-nuclease tether mediates Chi hotspot control of RecBCD enzyme
Abstract
In bacteria, repair of DNA double-strand breaks uses a highly conserved helicase-nuclease complex to unwind DNA from a broken end and cut it at specific DNA sequences called Chi. In Escherichia coli the RecBCD enzyme also loads the DNA strand-exchange protein RecA onto the newly formed end, resulting in a recombination hotspot at Chi. Chi hotspots regulate multiple RecBCD activities by altering RecBCD's conformation, which is proposed to include the swinging of the RecB nuclease domain on the 19-amino-acid tether connecting the helicase and nuclease domains. Here, we altered the tether and tested multiple RecBCD activities, genetically in cells and enzymatically in cell-free extracts. Randomizing the amino-acid sequence or lengthening it had little effect. However, shortening it by as little as two residues or making substitutions of ≥10 proline or ≥9 glycine residues dramatically lowered Chi-dependent activities. These results indicate that proper control of RecBCD by Chi requires that the tether be long enough and appropriately flexible. We discuss a model in which the swing-time of the nuclease domain determines the position of Chi-dependent and Chi-independent cuts and Chi hotspot activity.
Figures
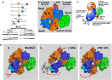
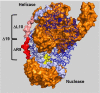
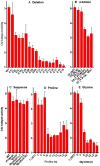
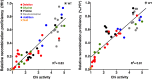
 ) from 3 to 17 independent experiments. Mutants are grouped by type: (A) deletion of amino acids; (B) addition of amino acids; (C) amino acid sequence changes; (D) substitutions with proline; (E) subsititutions with glycine.
) from 3 to 17 independent experiments. Mutants are grouped by type: (A) deletion of amino acids; (B) addition of amino acids; (C) amino acid sequence changes; (D) substitutions with proline; (E) subsititutions with glycine.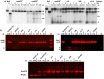
Similar articles
-
A flexible RecC surface loop required for Chi hotspot control of RecBCD enzyme.Genetics. 2023 Mar 2;223(3):iyac175. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac175. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 36521180 Free PMC article.
-
RecBCD Enzyme "Chi Recognition" Mutants Recognize Chi Recombination Hotspots in the Right DNA Context.Genetics. 2016 Sep;204(1):139-52. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.191056. Epub 2016 Jul 8. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27401752 Free PMC article.
-
Control of RecBCD enzyme activity by DNA binding- and Chi hotspot-dependent conformational changes.J Mol Biol. 2014 Oct 23;426(21):3479-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.07.017. Epub 2014 Jul 27. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25073102 Free PMC article.
-
RecBCD enzyme and the repair of double-stranded DNA breaks.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2008 Dec;72(4):642-71, Table of Contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00020-08. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2008. PMID: 19052323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro reconstitution of homologous recombination reactions.Experientia. 1994 Mar 15;50(3):204-15. doi: 10.1007/BF01924003. Experientia. 1994. PMID: 8143794 Review.
Cited by
-
Chi hotspot control of RecBCD helicase-nuclease by long-range intramolecular signaling.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 5;10(1):19415. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73078-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33154402 Free PMC article.
-
A flexible RecC surface loop required for Chi hotspot control of RecBCD enzyme.Genetics. 2023 Mar 2;223(3):iyac175. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac175. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 36521180 Free PMC article.
-
Omnipresent Maxwell's demons orchestrate information management in living cells.Microb Biotechnol. 2019 Mar;12(2):210-242. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13378. Microb Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30806035 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-complementation by the RecB nuclease domain of RecBCD enzyme reveals new insight into RecA loading upon χ recognition.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Mar 21;52(5):2578-2589. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae007. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38261972 Free PMC article.
-
E. coli RecB Nuclease Domain Regulates RecBCD Helicase Activity but not Single Stranded DNA Translocase Activity.J Mol Biol. 2024 Jan 15;436(2):168381. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168381. Epub 2023 Dec 9. J Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38081382 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

