Nuclear factor-kappa B-dependent X-box binding protein 1 signalling promotes the proliferation of nucleus pulposus cells under tumour necrosis factor alpha stimulation
- PMID: 30430692
- PMCID: PMC6496019
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12542
Nuclear factor-kappa B-dependent X-box binding protein 1 signalling promotes the proliferation of nucleus pulposus cells under tumour necrosis factor alpha stimulation
Abstract
Objectives: Tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) expressed by nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs) plays a critical role in intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration. A key unfolded protein response (UPR) component, X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) are essential for cell survival and proliferation. The aim of our study was to elucidate the roles of XBP1 and NF-κB in IVD degeneration (IDD).
Materials and methods: Rat NPCs were cultured with TNF-α in the presence or absence of XBP1 and NF-κB-p65 small interfering RNA. The associated genes and proteins were evaluated through quantitative real-time PCR, Western blot analyses and immunofluorescence staining to monitor UPR and NF-κB signalling and identify the regulatory mechanism of p65 by XBP1. Cell counting kit-8 assay, cell cycle analysis and related gene and protein expression were performed to examine the proliferation of NPCs.
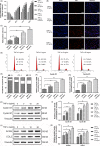
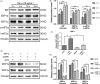
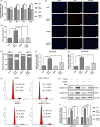
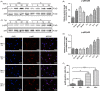
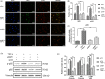
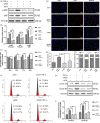
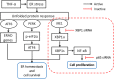
Results: The acute exposure of TNF-α accelerated the proliferation of rat NPCs by activating the UPR/XBP1 pathway. XBP1 signalling favoured the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of p65 subunit of NF-κB. The activation of NF-κB in the later phase also enhanced NPC proliferation.
Conclusions: Unfolded protein response reinforces the survival and proliferation of NPCs under TNF-α stimulation by activating the XBP1 pathway, and NF-κB serves as a vital mediator in these events. The XBP1 signalling of UPR can be a novel therapeutic target in IDD.
Keywords: NF-κB; TNF-α; nucleus pulposus; proliferation; unfolded protein response.
© 2018 The Authors. Cell Proliferation Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase/eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α pathway attenuates tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells by activating autophagy.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jul;234(7):11631-11645. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27820. Epub 2018 Dec 4. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30515797
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Facilitates the Survival and Proliferation of Nucleus Pulposus Cells in TNF-α Stimulus by Activating Unfolded Protein Response.DNA Cell Biol. 2018 Apr;37(4):347-358. doi: 10.1089/dna.2017.4029. Epub 2018 Jan 30. DNA Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29381432
-
The inflammatory cytokine TNF-α regulates the biological behavior of rat nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells through the NF-κB signaling pathway in vitro.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Aug;120(8):13664-13679. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28640. Epub 2019 Apr 2. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30938863
-
NF-κB signalling pathways in nucleus pulposus cell function and intervertebral disc degeneration.Cell Prolif. 2021 Jul;54(7):e13057. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13057. Epub 2021 May 24. Cell Prolif. 2021. PMID: 34028920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Function of NF-Kappa B During Epilepsy, a Potential Therapeutic Target.Front Neurosci. 2022 Mar 10;16:851394. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.851394. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35360161 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Associated Neuronal Death and Innate Immune Response in Neurological Diseases.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 10;12:794580. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.794580. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35082783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nimbolide targeting SIRT1 mitigates intervertebral disc degeneration by reprogramming cholesterol metabolism and inhibiting inflammatory signaling.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 May;13(5):2269-2280. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.02.018. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37250166 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress: An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 1;9:819139. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.819139. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35178406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory Effect of Inflammatory Mediators in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.Mediators Inflamm. 2023 Apr 17;2023:6210885. doi: 10.1155/2023/6210885. eCollection 2023. Mediators Inflamm. 2023. PMID: 37101594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumorous IRE1α facilitates CD8+T cells-dependent anti-tumor immunity and improves immunotherapy efficacy in melanoma.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 30;22(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01470-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38291473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jiang L, Zhang X, Zheng X, et al. Apoptosis, senescence, and autophagy in rat nucleus pulposus cells: Implications for diabetic intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(5):692‐702. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81572170/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81572190/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81702203/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2242016K40149/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province
- 2242017K3DN06/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

