The Role of IL-6RA in UHMWPE Promotes Proliferation in Fibro-Like Synovial Cells
- PMID: 30426007
- PMCID: PMC6217897
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/3928915
The Role of IL-6RA in UHMWPE Promotes Proliferation in Fibro-Like Synovial Cells
Abstract
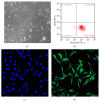
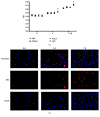
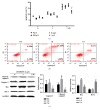
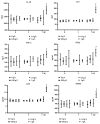
UHMWPE granule could induce macrophages and inflammatory responses in interfacial tissues, which eliminated the wear debris of UHMWPE component and further induced dissolution of the surrounding bone, leading aseptic loosening. However, the mechanism of synovial cells, especially fibroblast-like synovial (FLS) cells response to UHMWPE, remains unknown. Herein we choose FLS cells as research object. Vimentin (+) CD68 (-) was identified by flow cytometry and immunofluorescent staining assay, and the cells were identified as FLS cells, which was consistent with the experimental requirements. The inhibitory evaluation showed that UHMWPE could significantly promote the proliferation and inhibit apoptosis of FLS cells in dose- and time-dependent manners and increase the levels of proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, PGE2, MMP2, and LOX. UHMWPE also can induce the expression of mIL-6R protein in FLS cells and further investigate the relationship between apoptosis and inflammation. Interestingly enough, when we added the interleukin-6 receptor antagonist (IL-6RA), the expression levels of proapoptosis-related proteins increased; in other words, UHMWPE-induced antiapoptosis diminished by IL-6RA (50 μg/ml). Taken together, these findings clearly demonstrated that UHMWPE promote growth in FLS cells through upregulating inflammatory factors to produce antiapoptotic effect.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IL-6 trans-signalling directly induces RANKL on fibroblast-like synovial cells and is involved in RANKL induction by TNF-alpha and IL-17.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008 Nov;47(11):1635-40. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken363. Epub 2008 Sep 11. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008. PMID: 18786965
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of IL-6 production by Zc3h12a in fibroblast-like synovial cells.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011 Nov-Dec;29(6):906-12. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 22132693
-
Expression of cannabinoid receptor 2 and its inhibitory effects on synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014 May;53(5):802-9. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ket447. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014. PMID: 24440992
-
Mechano growth factor-E regulates apoptosis and inflammatory responses in fibroblast-like synoviocytes of knee osteoarthritis.Int Orthop. 2015 Dec;39(12):2503-9. doi: 10.1007/s00264-015-2974-5. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Int Orthop. 2015. PMID: 26338342
-
Flavonol-rich RVHxR from Rhus verniciflua Stokes and its major compound fisetin inhibits inflammation-related cytokines and angiogenic factor in rheumatoid arthritic fibroblast-like synovial cells and in vivo models.Int Immunopharmacol. 2009 Mar;9(3):268-76. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2008.11.005. Epub 2008 Dec 25. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19111632
References
-
- Keener J. D. Twenty-five-year results after Charnley total hip arthroplasty in patients less than fifty years old: a concise follow-up of a previous report. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery American Volume. 2014;96(21):1814–1819. - PubMed
-
- Miyanishi K., Trindade M. C., Goodman S. B., Schurman D. J., Smith R. L. Periprosthetic osteolysis: induction of vascular endothelial growth factor from human monocyte/macrophages by orthopaedic biomaterial particles. Journal of Bone & Mineral Research the Official Journal of the American Society for Bone & Mineral Research. 2003;18(9)1573 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

