Dose and Exposure Time-Dependent Renal and Hepatic Effects of Intraperitoneally Administered Fumonisin B₁ in Rats
- PMID: 30424021
- PMCID: PMC6265755
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins10110465
Dose and Exposure Time-Dependent Renal and Hepatic Effects of Intraperitoneally Administered Fumonisin B₁ in Rats
Abstract
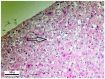
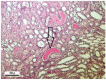
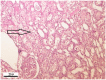
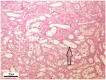
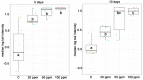
Male Wistar rats were treated intraperitoneally (i.p.) with fumonisin B₁ (FB₁; 0, 20, 50 and 100 mg/kg dietary dose equivalent) for 5 and 10 days (n = 24⁻24 in each setting) to gain dose- and time-dependent effects on antioxidant status and oxidative stress response, clinical chemical endpoints and liver, kidney and lung histopathology and lymphocyte damage (genotoxicity). FB₁ decreased feed intake, body weight gain and absolute liver weight, irrespective of the toxin dose. Relative kidney weight increased in the 10-day setting. Linear dose response was found for plasma aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, total cholesterol, urea and creatinine, and exposure time-dependence for plasma creatinine level. The latter was coupled with renal histopathological findings, tubular degeneration and necrosis and the detachment of tubular epithelial cells. The pronounced antioxidant response (reduced glutathione accretion, increasing glutathione peroxidase activity) referred to renal cortical response (5⁻10 days exposure at 50⁻100 ppm FB₁). Hepatic alterations were moderate, referring to initial phase lipid peroxidation (exposure time dependent difference of conjugated diene and triene concentrations), and slight functional disturbance (↑ total cholesterol). Lymphocyte DNA damage was moderate, supporting a mild genotoxic effect of FB₁.
Keywords: dose-dependence; fumonisin B1; genotoxicity; hepatotoxicity; nephrotoxicity; rat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effects of Mixed Fusarium Mycotoxins at EU-Permitted Feed Levels on Weaned Piglets' Tissue Lipids.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jun 27;13(7):444. doi: 10.3390/toxins13070444. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34199083 Free PMC article.
-
Mycotoxin fumonisin B1 alters cellular redox balance and signalling pathways in rat liver and kidney.Toxicology. 2007 Dec 5;242(1-3):31-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2007.09.006. Epub 2007 Sep 12. Toxicology. 2007. PMID: 17949882
-
Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of fumonisin B1 (cas no. 116355-83-0) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (feed studies).Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2001 Dec;(496):1-352. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2001. PMID: 11852482
-
Toxic Effects of Mycotoxin Fumonisin B1 at Six Different Doses on Female BALB/c Mice.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Dec 29;14(1):21. doi: 10.3390/toxins14010021. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35050998 Free PMC article.
-
Fumonisin B1 exposure increases Hsp70 expression in the lung and kidney of rats without inducing significant oxidative stress.Acta Vet Hung. 2018 Sep;66(3):394-407. doi: 10.1556/004.2018.036. Acta Vet Hung. 2018. PMID: 30264617
Cited by
-
Research Progress on Fumonisin B1 Contamination and Toxicity: A Review.Molecules. 2021 Aug 29;26(17):5238. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175238. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of chromatin-modifying enzymes and histone modifications in the modulation of p16 gene in fumonisin B1-induced toxicity in human kidney cells.Mycotoxin Res. 2023 Aug;39(3):271-283. doi: 10.1007/s12550-023-00494-2. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Mycotoxin Res. 2023. PMID: 37328702
-
The Effects of Mixed Fusarium Mycotoxins at EU-Permitted Feed Levels on Weaned Piglets' Tissue Lipids.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jun 27;13(7):444. doi: 10.3390/toxins13070444. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34199083 Free PMC article.
-
Response of Fecal Bacterial Flora to the Exposure of Fumonisin B1 in BALB/c Mice.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Aug 31;13(9):612. doi: 10.3390/toxins13090612. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34564616 Free PMC article.
-
Early-Life Exposure to the Mycotoxin Fumonisin B1 and Developmental Programming of the Ovary of the Offspring: The Possible Role of Autophagy in Fertility Recovery.Toxics. 2023 Dec 3;11(12):980. doi: 10.3390/toxics11120980. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 38133381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Commission (2003) Updated opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food (SCF) on Fumonisin B1, BIOMIN Mycotoxin Survey, (2017): BIOMIN Holding GmbH, Getzersdorf, Austria. [(accessed on 12 October 2018.)]; Available online: https://info.biomin.net/acton/attachment/14109/f-0463/1/-/-/l-0009/l-000....
-
- Kubena L., Edrington T., Harvey R., Buckley S., Phillips T., Rottinghaus G., Casper H. Individual and combined effects of fumonisin B1 present in Fusarium moniliforme culture material and T-2 toxin or deoxynivalenol in broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 1997;76:1239–1247. doi: 10.1093/ps/76.9.1239. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

