REX1 is the critical target of RNF12 in imprinted X chromosome inactivation in mice
- PMID: 30420655
- PMCID: PMC6232137
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07060-w
REX1 is the critical target of RNF12 in imprinted X chromosome inactivation in mice
Abstract
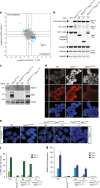
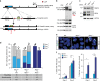
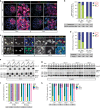
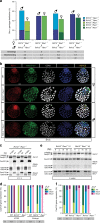
In mice, imprinted X chromosome inactivation (iXCI) of the paternal X in the pre-implantation embryo and extraembryonic tissues is followed by X reactivation in the inner cell mass (ICM) of the blastocyst to facilitate initiation of random XCI (rXCI) in all embryonic tissues. RNF12 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that plays a key role in XCI. RNF12 targets pluripotency protein REX1 for degradation to initiate rXCI in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and loss of the maternal copy of Rnf12 leads to embryonic lethality due to iXCI failure. Here, we show that loss of Rex1 rescues the rXCI phenotype observed in Rnf12-/- ESCs, and that REX1 is the prime target of RNF12 in ESCs. Genetic ablation of Rex1 in Rnf12-/- mice rescues the Rnf12-/- iXCI phenotype, and results in viable and fertile Rnf12-/-:Rex1-/- female mice displaying normal iXCI and rXCI. Our results show that REX1 is the critical target of RNF12 in XCI.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Roles of the Rlim-Rex1 axis during X chromosome inactivation in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Dec 26;120(52):e2313200120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2313200120. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 38113263 Free PMC article.
-
Rlim-Dependent and -Independent Pathways for X Chromosome Inactivation in Female ESCs.Cell Rep. 2017 Dec 26;21(13):3691-3699. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.12.004. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 29281819 Free PMC article.
-
RNF12 initiates X-chromosome inactivation by targeting REX1 for degradation.Nature. 2012 Apr 29;485(7398):386-90. doi: 10.1038/nature11070. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22596162
-
How does the Xist activator Rlim/Rnf12 regulate Xist expression?Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Jun 26;52(3):1099-1107. doi: 10.1042/BST20230573. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38747697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solving the "X" in embryos and stem cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2012 May 20;21(8):1215-24. doi: 10.1089/scd.2011.0685. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Stem Cells Dev. 2012. PMID: 22309156 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Molecular and Nuclear Dynamics of X-Chromosome Inactivation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2022 May 17;14(4):a040196. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a040196. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2022. PMID: 34312245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rlim/Rnf12, Rex1, and X Chromosome Inactivation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Oct 31;7:258. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00258. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31737626 Free PMC article.
-
A symmetric toggle switch explains the onset of random X inactivation in different mammals.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019 May;26(5):350-360. doi: 10.1038/s41594-019-0214-1. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30962582 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the Rlim-Rex1 axis during X chromosome inactivation in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Dec 26;120(52):e2313200120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2313200120. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 38113263 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin targeting of the RNF12/RLIM E3 ubiquitin ligase controls transcriptional responses.Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Jan 10;7(3):e202302282. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202302282. Print 2024 Mar. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 38199845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Monk M, McLaren A. X-chromosome activity in foetal germ cells of the mouse. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 1981;63:75–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

