Characterization of purinergic receptor expression in ARPKD cystic epithelia
- PMID: 30417216
- PMCID: PMC6298916
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-018-9632-5
Characterization of purinergic receptor expression in ARPKD cystic epithelia
Abstract
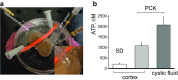
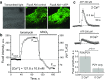
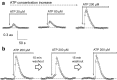
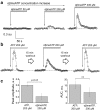
Polycystic kidney diseases (PKDs) are a group of inherited nephropathies marked by formation of fluid-filled cysts along the nephron. Growing evidence suggests that in the kidney formation of cysts and alteration of cystic electrolyte transport are associated with purinergic signaling. PCK/CrljCrl-Pkhd1pck/CRL (PCK) rat, an established model of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), was used here to test this hypothesis. Cystic fluid of PCK rats and their cortical tissues exhibited significantly higher levels of ATP compared to Sprague Dawley rat kidney cortical interstitium as assessed by highly sensitive ATP enzymatic biosensors. Confocal calcium imaging of the freshly isolated cystic monolayers revealed a stronger response to ATP in a higher range of concentrations (above 100 μM). The removal of extracellular calcium results in the profound reduction of the ATP evoked transient, which suggests calcium entry into the cyst-lining cells is occurring via the extracellular (ionotropic) P2X channels. Further use of pharmacological agents (α,β-methylene-ATP, 5-BDBD, NF449, isoPPADS, AZ10606120) and immunofluorescent labeling of isolated cystic epithelia allowed us to narrow down potential candidate receptors. In conclusion, our ex vivo study provides direct evidence that the profile of P2 receptors is shifted in ARPKD cystic epithelia in an age-related manner towards prevalence of P2X4 and/or P2X7 receptors, which opens new avenues for the treatment of this disease.
Keywords: ARPKD; ATP; Intracellular calcium flux; Kidney; P2X receptors; P2X4; P2X7; P2rx4; P2rx7; PCK rat; Polycystic kidney disease; Purinergic receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Oleg Palygin declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Daria V. Ilatovskaya declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Vladislav Levchenko declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Christine A. Klemens declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Lashodya Dissanayake declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Anna Marie Williams declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Tengis S. Pavlov declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Alexander Staruschenko declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Animal use and welfare adhered to the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals following a protocol reviewed and approved by the IACUC at the Medical College of Wisconsin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Knockout of P2rx7 purinergic receptor attenuates cyst growth in a rat model of ARPKD.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Dec 1;317(6):F1649-F1655. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00395.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31630543 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of P2X4 receptor activity by ivermectin and 5-BDBD has no effect on the development of ARPKD in PCK rats.Physiol Rep. 2022 Nov;10(21):e15510. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15510. Physiol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36353932 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular ATP Induces Calcium Signaling in Odontoblasts.J Dent Res. 2017 Feb;96(2):200-207. doi: 10.1177/0022034516671308. Epub 2016 Oct 2. J Dent Res. 2017. PMID: 27694154
-
P2X4: A fast and sensitive purinergic receptor.Biomed J. 2017 Oct;40(5):245-256. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2017.06.010. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Biomed J. 2017. PMID: 29179879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional and therapeutic importance of purinergic signaling in polycystic kidney disease.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Dec 1;311(6):F1135-F1139. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00406.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27654892 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vibrodissociation method for isolation of defined nephron segments from human and rodent kidneys.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Nov 1;317(5):F1398-F1403. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00448.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31588797 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase-1 and the inflammasome promote polycystic kidney disease progression.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Nov 29;9:971219. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.971219. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36523654 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Nucleotides and P2 Receptors in Renal Function.Physiol Rev. 2020 Jan 1;100(1):211-269. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00038.2018. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Physiol Rev. 2020. PMID: 31437091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in understanding ion transport mechanisms in polycystic kidney disease.Clin Sci (Lond). 2021 Nov 12;135(21):2521-2540. doi: 10.1042/CS20210370. Clin Sci (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34751394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of ceramide biosynthesis in increased extracellular vesicle release in Pkd1 knock out cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 10;13:1005639. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1005639. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36299464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torres VE, Harris PC. Mechanisms of disease: autosomal dominant and recessive polycystic kidney diseases. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2006;2(1):40–55. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann C, Senderek J, Kupper F, Schneider F, Dornia C, Windelen E, Eggermann T, Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Kirfel J, Furu L, Onuchic LF, Rossetti S, Harris PC, Somlo S, Guay-Woodford L, Germino GG, Moser M, Buttner R, Zerres K. PKHD1 mutations in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) Hum Mutat. 2004;23(5):453–463. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy C, Chootip K, Mitchell C, Syed NI, Tengah A. P2X and P2Y nucleotide receptors as targets in cardiovascular disease. Future Med Chem. 2013;5(4):431–449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

