The Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis Based on Human Signaling Networks and Stem Cell Expression Data
- PMID: 30416382
- PMCID: PMC6216023
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.27896
The Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis Based on Human Signaling Networks and Stem Cell Expression Data
Abstract
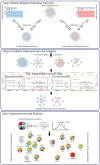
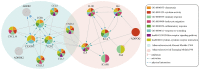
Atherosclerosis is a common and complex disease, whose morbidity increased significantly. Here, an integrated approach was proposed to elucidate systematically the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis from a systems biology point of view. Two weighted human signaling networks were constructed based on atherosclerosis related gene expression data of stem cells. Then, 37 candidate Atherosclerosis-risk Modules were detected using four kinds of permutation tests. Five Atherosclerosis-risk Modules (three Absent Modules and two Emerging Modules) enriched in functions significantly associated with disease genes were identified and verified to be associated with the maintenance of normal biological process and the pathogenesis and development of atherosclerosis. Especially for Atherosclerosis-risk Emerging Module P96, it could distinguish between normal and disease samples by Supporting Vector Machine with the average expression value of the module as classification feature. These identified modules and their genes may act as potential atherosclerosis biomarkers. Our study would shed light on the signal transduction of atherosclerosis, and provide new insights to its pathogenesis from the perspective of stem cells.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; expression data; human signaling network; module; stem cell.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Observation of significant biomarkers in osteosarcoma via integrating module- identification method with attract.Cancer Biomark. 2017 Jul 19;20(1):87-93. doi: 10.3233/CBM-170144. Cancer Biomark. 2017. PMID: 28759958
-
Identification of melanoma biomarkers based on network modules by integrating the human signaling network with microarrays.J Cancer Res Ther. 2014 Nov;10 Suppl:C114-24. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.145816. J Cancer Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25450268
-
Integrated module and gene-specific regulatory inference implicates upstream signaling networks.PLoS Comput Biol. 2013;9(10):e1003252. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003252. Epub 2013 Oct 17. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013. PMID: 24146602 Free PMC article.
-
The use of network analyses for elucidating mechanisms in cardiovascular disease.Mol Biosyst. 2010 Feb;6(2):289-304. doi: 10.1039/b912078e. Epub 2009 Oct 16. Mol Biosyst. 2010. PMID: 20094647 Review.
-
From blastocyst to gastrula: gene regulatory networks of embryonic stem cells and early mouse embryogenesis.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Dec 5;369(1657):20130542. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0542. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25349451 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying significant genes and functionally enriched pathways in familial hypercholesterolemia using integrated gene co-expression network analysis.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 May;29(5):3287-3299. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.02.002. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35844366 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalin inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells by regulating the MEG3/p53 pathway following treatment with ox‑LDL.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Feb;43(2):901-913. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.4009. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30535498 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Cardiology and Atherosclerosis in the Context of Precision Medicine: A Scoping Review.Appl Bionics Biomech. 2024 Apr 30;2024:2991243. doi: 10.1155/2024/2991243. eCollection 2024. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2024. PMID: 38715681 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buckley ML, Ramji DP. The influence of dysfunctional signaling and lipid homeostasis in mediating the inflammatory responses during atherosclerosis. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2015;1852:1498–510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

