The critical role of AMPK in driving Akt activation under stress, tumorigenesis and drug resistance
- PMID: 30413706
- PMCID: PMC6226490
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07188-9
The critical role of AMPK in driving Akt activation under stress, tumorigenesis and drug resistance
Abstract
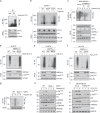
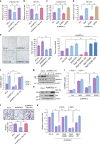
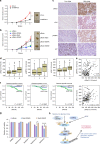
PI3K/Akt signaling is activated in cancers and governs tumor initiation and progression, but how Akt is activated under diverse stresses is poorly understood. Here we identify AMPK as an essential regulator for Akt activation by various stresses. Surprisingly, AMPK is also activated by growth factor EGF through Ca2+/Calmodulin-dependent kinase and is essential for EGF-mediated Akt activation and biological functions. AMPK phosphorylates Skp2 at S256 and promotes the integrity and E3 ligase activity of Skp2 SCF complex leading to K63-linked ubiquitination and activation of Akt and subsequent oncogenic processes. Importantly, AMPK-mediated Skp2 S256 phosphorylation promotes breast cancer progression in mouse tumor models, correlates with Akt and AMPK activation in breast cancer patients, and predicts poor survival outcomes. Finally, targeting AMPK-mediated Skp2 S256 phosphorylation sensitizes cells to anti-EGF receptor targeted therapy. Our study sheds light on how stress and EGF induce Akt activation and new mechanisms for AMPK-mediated oncogenesis and drug resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Skp2-SCF E3 ligase regulates Akt ubiquitination, glycolysis, herceptin sensitivity, and tumorigenesis.Cell. 2012 May 25;149(5):1098-111. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.065. Cell. 2012. PMID: 22632973 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombin and histamine stimulate endothelial nitric-oxide synthase phosphorylation at Ser1177 via an AMPK mediated pathway independent of PI3K-Akt.FEBS Lett. 2004 Aug 27;573(1-3):175-80. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.07.078. FEBS Lett. 2004. PMID: 15327994
-
Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of cytosolic localization and oncogenic function of Skp2 by Akt/PKB.Nat Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;11(4):420-32. doi: 10.1038/ncb1849. Epub 2009 Mar 8. Nat Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19270694 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into Notch1 regulation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR1 signaling axis: targeted therapy of γ-secretase inhibitor resistant T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cell Signal. 2014 Jan;26(1):149-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.09.021. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24140475 Review.
-
AMPK and Cancer.Exp Suppl. 2016;107:203-226. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-43589-3_9. Exp Suppl. 2016. PMID: 27812982 Review.
Cited by
-
The Distinct Roles of LKB1 and AMPK in p53-Dependent Apoptosis Induced by Cisplatin.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 2;23(17):10064. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710064. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077459 Free PMC article.
-
Telomerase RNA TERC and the PI3K-AKT pathway form a positive feedback loop to regulate cell proliferation independent of telomerase activity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Apr 22;50(7):3764-3776. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac179. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35323972 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Activities of Ceratonia siliqua Pod and Seed Extracts: A Comparative Analysis of Two Cretan Cultivars.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 28;24(15):12104. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512104. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569477 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic restraint stress promotes gastric epithelial malignant transformation by activating the Akt/p53 signaling pathway via ADRB2.Oncol Lett. 2022 Jul 5;24(3):300. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13420. eCollection 2022 Sep. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35949623 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of miR-34c in Hypoxia by Activating Autophagy through BCL2 Repression.Mol Cells. 2022 Jun 30;45(6):403-412. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2022.2010. Mol Cells. 2022. PMID: 35611688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- LC. C. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science. 2001;296:1655–1657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

