Perspective on nanochannels as cellular mediators in different disease conditions
- PMID: 30409198
- PMCID: PMC6222982
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-018-0281-7
Perspective on nanochannels as cellular mediators in different disease conditions
Abstract
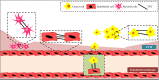
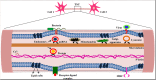
Tunnelling nanotubes (TNTs), also known as membrane nanochannels, are actin-based structures that facilitate cytoplasmic connections for rapid intercellular transfer of signals, organelles and membrane components. These dynamic TNTs can form de novo in animal cells and establish complex intercellular networks between distant cells up to 150 μm apart. Within the last decade, TNTs have been discovered in different cell types including tumor cells, macrophages, monocytes, endothelial cells and T cells. It has also been further elucidated that these nanotubes play a vital role in diseased conditions such as cancer, where TNT formation occurs at a higher pace and is used for rapid intercellular modulation of chemo-resistance. Viruses such as HIV, HSV and prions also hijack the existing TNT connections between host cells for rapid transmission and evasion of the host immune responses. The following review aims to describe the heterogeneity of TNTs, their role in different tissues and disease conditions in order to enhance our understanding on how these nanotubes can be used as a target for therapies.
Keywords: Tumor-endothelial interaction; Tumor-immune cell interaction; Tumor-macrophages cell-cell communication; Tunneling nanotubes (TNTs).
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
AG is an employee of Mitra Biotech and holds equity. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wiring through tunneling nanotubes--from electrical signals to organelle transfer.J Cell Sci. 2012 Mar 1;125(Pt 5):1089-98. doi: 10.1242/jcs.083279. Epub 2012 Mar 7. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22399801 Review.
-
Macrophage conditioned medium induced cellular network formation in MCF-7 cells through enhanced tunneling nanotube formation and tunneling nanotube mediated release of viable cytoplasmic fragments.Exp Cell Res. 2017 Jun 15;355(2):182-193. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.04.008. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Exp Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28412243
-
Chlamydia trachomatis Cell-to-Cell Spread through Tunneling Nanotubes.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0281722. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02817-22. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36219107 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-level communication of human retinal pigment epithelial cells via tunneling nanotubes.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033195. Epub 2012 Mar 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22457742 Free PMC article.
-
Tunneling nanotubes: The intercellular conduits contributing to cancer pathogenesis and its therapy.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023 Nov;1878(6):189028. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.189028. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37993000 Review.
Cited by
-
Myo1d promotes alpha-synuclein transfer from brain microvascular endothelial cells to pericytes through tunneling nanotubes.iScience. 2023 Jul 22;26(8):107458. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107458. eCollection 2023 Aug 18. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37575183 Free PMC article.
-
Tunneling Nanotubes and the Eye: Intercellular Communication and Implications for Ocular Health and Disease.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Apr 8;2020:7246785. doi: 10.1155/2020/7246785. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32352005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secretome and Tunneling Nanotubes: A Multilevel Network for Long Range Intercellular Communication between Endothelial Cells and Distant Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 26;22(15):7971. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157971. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-1β Induces Intracellular Serum Amyloid A1 Expression in Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells and Promotes its Intercellular Exchange.Inflammation. 2019 Aug;42(4):1413-1425. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01003-3. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 31011929
-
Tumor Cell Communications as Promising Supramolecular Targets for Cancer Chemotherapy: A Possible Strategy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 27;25(19):10454. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910454. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408784 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lou E, Fujisawa S, Morozov A, Barlas A, Romin Y, Dogan Y, Gholami S, Moreira AL, Manova-Todorova K, Moore MA. Tunneling nanotubes provide a unique conduit for intercellular transfer of cellular contents in human malignant pleural mesothelioma. PLoS One. 2012;7:e33093. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033093. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abounit S, Zurzolo C. Wiring through tunneling nanotubes–from electrical signals to organelle transfer. J Cell Sci. 2012;jcs:083279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

