Structural basis of Gip1 for cytosolic sequestration of G protein in wide-range chemotaxis
- PMID: 30401901
- PMCID: PMC6219514
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07035-x
Structural basis of Gip1 for cytosolic sequestration of G protein in wide-range chemotaxis
Abstract
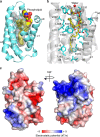
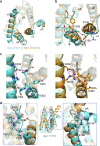
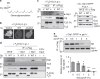
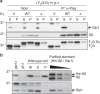
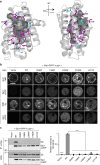
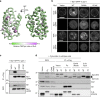
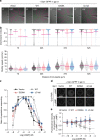
G protein interacting protein 1 (Gip1) binds and sequesters heterotrimeric G proteins in the cytosolic pool, thus regulating G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signalling for eukaryotic chemotaxis. Here, we report the underlying structural basis of Gip1 function. The crystal structure reveals that the region of Gip1 that binds to the G protein has a cylinder-like fold with a central hydrophobic cavity composed of six α-helices. Mutagenesis and biochemical analyses indicate that the hydrophobic cavity and the hydrogen bond network at the entrance of the cavity are essential for complex formation with the geranylgeranyl modification on the Gγ subunit. Mutations of the cavity impair G protein sequestration and translocation to the membrane from the cytosol upon receptor stimulation, leading to defects in chemotaxis at higher chemoattractant concentrations. These results demonstrate that the Gip1-dependent regulation of G protein shuttling ensures wide-range gradient sensing in eukaryotic chemotaxis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heterotrimeric G-protein shuttling via Gip1 extends the dynamic range of eukaryotic chemotaxis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Apr 19;113(16):4356-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1516767113. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27044073 Free PMC article.
-
GPCR Signaling Regulation in Dictyostelium Chemotaxis.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2274:317-336. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1258-3_27. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34050483
-
Imaging G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR)-mediated signaling events that control chemotaxis of Dictyostelium discoideum.J Vis Exp. 2011 Sep 20;(55):3128. doi: 10.3791/3128. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 21969095 Free PMC article.
-
Gradient sensing during chemotaxis.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;25(5):532-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jul 20. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23880435 Review.
-
Function and Regulation of Heterotrimeric G Proteins during Chemotaxis.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jan 14;17(1):90. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010090. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26784171 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cells function as a ternary logic gate to decide migration direction under integrated chemical and fluidic cues.Lab Chip. 2023 Feb 14;23(4):631-644. doi: 10.1039/d2lc00807f. Lab Chip. 2023. PMID: 36524874 Free PMC article.
-
Signal processing capacity of the cellular sensory machinery regulates the accuracy of chemotaxis under complex cues.iScience. 2021 Oct 7;24(11):103242. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103242. eCollection 2021 Nov 19. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34746705 Free PMC article.
-
Different Heterotrimeric G Protein Dynamics for Wide-Range Chemotaxis in Eukaryotic Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 3;9:724797. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.724797. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34414196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of FNDC1 suppresses gastric cancer progression by interfering with Gβγ-VEGFR2 complex formation.iScience. 2023 Aug 12;26(9):107534. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107534. eCollection 2023 Sep 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37670789 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

