Radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for breast cancer liver metastasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30387333
- PMCID: PMC6238116
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1700516
Radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for breast cancer liver metastasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note to: Radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for breast cancer liver metastasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022 Jun 15;23(6):528. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B17r0516. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022. PMID: 35686530 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the comparative therapeutic efficacy of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and hepatic resection (HR) for breast cancer liver metastases (BCLMs).
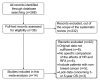
Methods: Studies that had examined the outcomes for both RFA and HR for BCLM were identified by searching the electronic databases PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library. Pooled analyzes of the overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), and short-term outcomes of BCLM were performed.
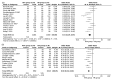
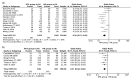
Results: Patients with BCLM gained many more survival benefits from HR than from RFA with regard to the 3-year OS rate (combined odds ratio (OR) 0.41, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.29-0.59, P<0.001), 5-year OS rate (combined OR 0.38, 95% CI 0.32-0.46, P<0.001), 3-year DFS (combined OR 0.36, 95% CI 0.27-0.49, P<0.001), and 5-year DFS (combined OR 0.51, 95% CI 0.40-0.66, P<0.001). RFA had fewer postoperative complications (combined OR 0.30, 95% CI 0.20-0.44, P<0.001) and shorter hospital stays (combined OR -9.01, 95% CI -13.49-4.54, P<0.001) than HR.
Conclusions: HR takes precedence over RFA in the treatment of patients with BCLM, considering the better survival rate. RFA gives rise to fewer complications and can be carried out with a shorter hospital stay, compared to HR. RFA should be reserved for patients who are not optimum candidates for resection.
Keywords: Breast cancer liver metastasis; Radiofrequency ablation; Hepatic resection; Prognosis; Meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Figures

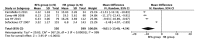

Similar articles
-
Comparison of liver resection and radiofrequency ablation in long-term survival among patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of randomized trials and high-quality propensity score-matched studies.World J Surg Oncol. 2024 Feb 19;22(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03330-8. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38369480 Free PMC article.
-
The prognosis of radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for patients with colorectal liver metastases: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on 22 studies.Int J Surg. 2021 Mar;87:105896. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.105896. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Int J Surg. 2021. PMID: 33588125
-
Radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for small hepatocellular carcinomas: a meta-analysis of randomized and nonrandomized controlled trials.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 3;9(1):e84484. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084484. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24404166 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-arterial chemoembolization + radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection in hepatocellular carcinoma - A meta-analysis.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2020 May;46(5):763-771. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2020.01.004. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31937433 Review.
-
Radiofrequency (thermal) ablation versus no intervention or other interventions for hepatocellular carcinoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Dec 19;(12):CD003046. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003046.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24357457 Review.
Cited by
-
The global status of research in breast cancer liver metastasis: a bibliometric and visualized analysis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):12246-12262. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2006552. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34783637 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Techniques in the Percutaneous Ablation of Liver Tumours.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Mar 24;11(4):585. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11040585. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RIG-I Promotes Cell Death in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Inducing M1 Polarization of Perineal Macrophages Through the RIG-I/MAVS/NF-κB Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Sep 3;13:8783-8794. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S258450. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32982277 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of radio frequency ablation and routine resection in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021 Apr;12(2):770-780. doi: 10.21037/jgo-21-52. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34012665 Free PMC article.
-
Retraction Note to: Radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for breast cancer liver metastasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022 Jun 15;23(6):528. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B17r0516. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022. PMID: 35686530 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

