Recovery of natural killer cells is mainly in post-treatment period in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with sofosbuvir plus ledipasvir
- PMID: 30386105
- PMCID: PMC6209576
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i40.4554
Recovery of natural killer cells is mainly in post-treatment period in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with sofosbuvir plus ledipasvir
Abstract
Aim: To investigate how natural killer (NK) cells are affected in the elimination of hepatitis C virus (HCV) by sofosbuvir/ledipasvir, two highly effective direct-acting antivirals (DAAs).
Methods: Thirteen treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients were treated with sofosbuvir/ledipasvir, and NK cells were detected at baseline, weeks 2, 4, 8 and 12 during therapy, and week post of treatment (Pt)-12 and 24 after the end of therapy by multicolor flow cytometry and compared with those from 13 healthy controls.
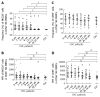
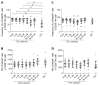
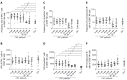
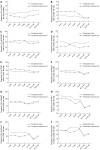
Results: All patients achieved sustained virological response. There was a significant decline in CD56bright NK cell frequencies at week 8 (P = 0.002) and week 12 (P = 0.003), which were altered to the level comparable to healthy controls at week Pt-12, but no difference was observed in the frequency of CD56dim NK cells. Compared with healthy controls, the expression levels of NKG2A, NKp30 and CD94 on NK cells from CHC patients at baseline were higher. NKG2A, NKp30 and CD94 started to recover at week 12 and reached the levels similar to those of healthy controls at week Pt-12 or Pt-24. Before treatment, patients have higher interferon (IFN)-γ and perforin levels than healthy controls, and IFN-γ started to recover at week 8 and reached the normalized level at week Pt-12.
Conclusion: NK cells of CHC patients can be affected by DAAs, and phenotypes and function of NK cells recover not at early stage but mainly after the end of sofosbuvir/ledipasvir treatment.
Keywords: Direct-acting antivirals therapy; Hepatitis C virus; Natural killer cells; Natural killer subsets.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: To the best of our knowledge, no conflict of interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Direct antiviral agents upregulate natural killer cell potential activity in chronic hepatitis C patients.Clin Exp Med. 2019 Aug;19(3):299-308. doi: 10.1007/s10238-019-00564-9. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Clin Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 31218578
-
Treatment with sofosbuvir and ledipasvir without ribavirin for 12 weeks is highly effective for recurrent hepatitis C virus genotype 1b infection after living donor liver transplantation: a Japanese multicenter experience.J Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug;52(8):986-991. doi: 10.1007/s00535-017-1310-9. Epub 2017 Jan 30. J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28138756
-
Efficacy of Ledipasvir Plus Sofosbuvir for 8 or 12 Weeks in Patients With Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 2 Infection.Gastroenterology. 2017 May;152(6):1366-1371. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.01.017. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Gastroenterology. 2017. PMID: 28137593 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of once daily ledipasvir/sofosbuvir fixed-dose combination in patients with chronic hepatitis C.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2016;15(4):549-57. doi: 10.1517/14740338.2016.1157163. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2016. PMID: 26899025 Review.
-
Combination of Ledipasvir and Sofosbuvir for Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 1 Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Ann Hepatol. 2017 March-April;16(2):188-197. doi: 10.5604/16652681.1231562. Ann Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28233739 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
CD4/CD8 Ratio could be predictor of burden hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian chronic hepatitis C after combined sofosbuvir and daclatasvir therapy.Afr Health Sci. 2023 Mar;23(1):198-212. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v23i1.22. Afr Health Sci. 2023. PMID: 37545943 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19: Characteristics and Therapeutics.Cells. 2021 Jan 21;10(2):206. doi: 10.3390/cells10020206. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33494237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis C Virus and the Host: A Mutual Endurance Leaving Indelible Scars in the Host's Immunity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 23;25(1):268. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010268. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversal of Immunity After Clearance of Chronic HCV Infection-All Reset?Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 8;11:571166. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.571166. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33133084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconstitution of T follicular helper-humoral immune axis with elimination of hepatitis C virus.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 16;10(1):19924. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77020-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33199783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. 2017. Hepatitis C. Available on October 13, 2017. Updated July. Available from: URL: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs164/en/
-
- Lee MH, Yang HI, Lu SN, Jen CL, You SL, Wang LY, Wang CH, Chen WJ, Chen CJ; R. E.V.E.A.L.-HCV Study Group. Chronic hepatitis C virus infection increases mortality from hepatic and extrahepatic diseases: a community-based long-term prospective study. J Infect Dis. 2012;206:469–477. - PubMed
-
- Hadziyannis SJ, Sette H Jr, Morgan TR, Balan V, Diago M, Marcellin P, Ramadori G, Bodenheimer H Jr, Bernstein D, Rizzetto M, Zeuzem S, Pockros PJ, Lin A, Ackrill AM; PEGASYS International Study Group. Peginterferon-alpha2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:346–355. - PubMed
-
- Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, Smith C, Marinos G, Gonçales FL Jr, Häussinger D, Diago M, Carosi G, Dhumeaux D, Craxi A, Lin A, Hoffman J, Yu J. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:975–982. - PubMed
-
- Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Rustgi VK, Shiffman M, Reindollar R, Goodman ZD, Koury K, Ling M, Albrecht JK. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001;358:958–965. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

