Survivin regulates chromosome segregation by modulating the phosphorylation of Aurora B during porcine oocyte meiosis
- PMID: 30382773
- PMCID: PMC6342075
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1542894
Survivin regulates chromosome segregation by modulating the phosphorylation of Aurora B during porcine oocyte meiosis
Abstract
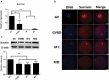
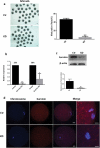
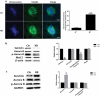
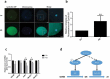
SURVIVIN is an essential chromosomal passenger complex (CPC) subunit and participates in cell division. In this study, we used porcine oocyte as a model to investigate the roles of Survivin during porcine oocyte maturation. Survivin was highly expressed in germinal vesicle (GV) and germinal vesicle breakdown (GVBD) stages oocytes, mainly localized in the GV at GV stage and on the chromosomes after GVBD. We have used RNA interference to specifically deplete Survivin in oocytes during in vitro maturation (IVM). Immunofluorescence assay showed that Survivin-depleted oocytes failed to produce polar body in meiosisⅠ (failed to complete cytokinesis), and they were arrested in metaphaseⅠwith misaligned chromosomes. The homologous chromosomes in Survivin-depleted oocytes could not be separated normally. Moreover, both the phosphorylation levels of Aurora B and the mRNA level of Mad2L1 related to spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) was decreased in Survivin-depleted oocytes, which thus inhibited the degradation of Cyclin B1 (CCNB1) to complete meiosis. Taken together, we conclude that Survivin is an important mediator of centromere and midbody docking of Aurora-B as well as its activity and regulates SAC and MPF activity during meiosis in porcine oocytes.
Keywords: Survivin; chromosomes; metaphase I; oocyte; pig; spindle assembly checkpoint.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aurora B inhibitor barasertib prevents meiotic maturation and subsequent embryo development in pig oocytes.Theriogenology. 2016 Jul 15;86(2):503-15. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2016.01.030. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Theriogenology. 2016. PMID: 26993175
-
MCAK is present at centromeres, midspindle and chiasmata and involved in silencing of the spindle assembly checkpoint in mammalian oocytes.Mol Hum Reprod. 2010 Sep;16(9):665-84. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaq025. Epub 2010 Apr 20. Mol Hum Reprod. 2010. PMID: 20406800
-
CDCA8 regulates meiotic spindle assembly and chromosome segregation during human oocyte meiosis.Gene. 2020 May 30;741:144495. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144495. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32088244
-
[Molecular Mechanism of Aurora Kinase A Regulating the Meiosis of Oocyte].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2022 Feb;44(1):142-148. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.13811. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35300777 Review. Chinese.
-
Spindle assembly and chromosome dynamics during oocyte meiosis.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2019 Oct;60:53-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2019.03.014. Epub 2019 May 10. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31082633 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rescue in vitro maturation using ovarian support cells of human oocytes from conventional stimulation cycles yields oocytes with improved nuclear maturation and transcriptomic resemblance to in vivo matured oocytes.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024 Aug;41(8):2021-2036. doi: 10.1007/s10815-024-03143-4. Epub 2024 May 30. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024. PMID: 38814543 Free PMC article.
-
ALKBH5 controls the meiosis-coupled mRNA clearance in oocytes by removing the N 6-methyladenosine methylation.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 17;14(1):6532. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42302-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37848452 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of survivin induces spindle disorganization, chromosome misalignment, and DNA damage during mouse embryo development.Cell Cycle. 2020 Sep;19(17):2148-2157. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1794545. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 32687433 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of neddylation causes meiotic arrest in mouse oocyte.Cell Cycle. 2019 Jun;18(11):1254-1267. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1617453. Epub 2019 May 21. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 31111756 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular determinants of the meiotic arrests in mammalian oocytes at different stages of maturation.Cell Cycle. 2022 Mar-Mar;21(6):547-571. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2026704. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Cell Cycle. 2022. PMID: 35072590 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altieri DC. Validating survivin as a cancer therapeutic target. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003. January 3;1:46–54. PubMed PMID: WOS:000180448400014; English. - PubMed
-
- Jeyaprakash AA, Klein UR, Lindner D, et al. Structure of a Survivin-Borealin-INCENP core complex reveals how chromosomal passengers travel together. Cell. 2007. October 19;131(2):271–285. PubMed PMID: WOS:000250507700018; English. - PubMed
-
- Adams RR, Carmena M, Earnshaw WC. Chromosomal passengers and the (aurora) ABCs of mitosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2001. February;11(2):49–54. PubMed PMID: 11166196. - PubMed
-
- Vagnarelli P, Earnshaw WC. Chromosomal passengers: the four-dimensional regulation of mitotic events. Chromosoma. 2004. November;113(5):211–222. PubMed PMID: 15351889. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
