A New Explanation of Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients With Respect to Claudin-5, Matrix Metalloproteinase-9, and Neuroserpin
- PMID: 30375560
- PMCID: PMC6190976
- DOI: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2016.5974
A New Explanation of Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients With Respect to Claudin-5, Matrix Metalloproteinase-9, and Neuroserpin
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to investigate the relationship between neuroserpin (NSP) and claudin-5, as well as matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), with respect to clinical activity of disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Patients and methods: The study included a total of 75 patients (18 males, 57 females; mean age 48.12±11.23 years; range 20 to 60 years) who were admitted to the rheumatology outpatient facility at the Medical Faculty Hospital, Sakarya University, in October 2014. Patients were divided into four groups based on their Disease Activity Score 28 (DAS28) scores as remission group (n=16, DAS28 <2.6), low disease activity group (n=16, DAS28 between 2.6-3.2), moderate disease activity group (n=28, DAS28 between 3.2-5.1), and high disease activity group (n=15, DAS28 >5.1). Ten healthy subjects (HS) served as controls.
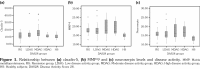
Results: Claudin-5, MMP-9, and NSP levels were significantly different in rheumatoid arthritis patients compared to HS (p=0.035, 0.026, and 0.014, respectively). Additionally, there were no differences between claudin-5 levels and disease activity among all RA groups. However, compared to HS, patient groups showed a significant difference (p=0.035) in terms of claudin-5 levels. Serum levels of MMP-9 were significantly different in moderate disease activity group compared to HS (p=0.013). Levels of NSP were significantly different in moderate disease activity and high disease activity groups compared to HS (p=0.008 and 0.031, respectively).
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated the differential associations of endothelial function/dysfunction biomarkers and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. How and why this impairment occurs is not fully understood and more data regarding NSP, MMP, and claudin expression in plasma are warranted.
Keywords: Claudin-5; matrix metalloproteinase-9; neuroserpin; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-3 levels in relation to disease activity and radiological progression in rheumatoid arthritis.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019 May;28(5):665-670. doi: 10.17219/acem/94065. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 30740946
-
Roles of claudin-5 and von Willebrand factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Feb 1;8(2):1979-84. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25973092 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-3 and the 7-joint ultrasound score in the assessment of disease activity and therapeutic efficacy in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Nov 15;19(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1449-z. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29141665 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Intensive therapy for moderate established rheumatoid arthritis: the TITRATE research programme.Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2021 Aug. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2021 Aug. PMID: 34406722 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Down-titration and discontinuation strategies of tumor necrosis factor-blocking agents for rheumatoid arthritis in patients with low disease activity.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Sep 29;(9):CD010455. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010455.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 May 24;5:CD010455. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010455.pub3 PMID: 25264908 Updated. Review.
Cited by
-
Serum Col3-4: A new type III and IV collagen biochemical marker of synovial tissue turnover in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 13;18(4):e0282954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282954. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37053217 Free PMC article.
-
The probable role of tissue plasminogen activator/neuroserpin axis in Alzheimer's disease: a new perspective.Acta Neurol Belg. 2024 Apr;124(2):377-388. doi: 10.1007/s13760-023-02403-x. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Acta Neurol Belg. 2024. PMID: 37917293 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad SF, Zoheir KM, Bakheet SA, Ashour AE, Attia SM. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor modulates T regulatory and IL-17 cells in the prevention of adjuvant induced arthritis in mice model. Cytokine. 2014;68:76–85. - PubMed
-
- Brahn E, Lee S, Lucas A, McFadden G, Macaulay C. Suppression of collagen-induced arthritis with a serine proteinase inhibitor (serpin) derived from myxoma virus. Clin Immunol. 2014;153:254–263. - PubMed
-
- Okazaki H, Lin Q, Nishikawa K, Ohtsuji N, Tsurui H, Ohtsuji M, et al. TNFa but not IL-17 is critical in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis spontaneously occurring in a unique FcgRIIB-deficient mouse model. Mod Rheumatol. 2014;24:931–938. - PubMed
-
- Choi JH, Lee JH, Roh KH, Seo SK, Choi IW, Park SG, et al. Gallium nitrate ameliorates type II collagen- induced arthritis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;20:269–275. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
