Reconsolidation/destabilization, extinction and forgetting of fear memory as therapeutic targets for PTSD
- PMID: 30374892
- PMCID: PMC6373183
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-018-5086-2
Reconsolidation/destabilization, extinction and forgetting of fear memory as therapeutic targets for PTSD
Abstract
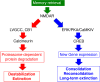
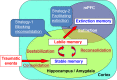
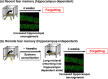
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a psychiatric disorder associated with memories of traumatic experiences. Conditioned fear memory, a representative model of traumatic memories, is observed across species from lower to higher animals, including humans. Numerous studies have investigated the mechanisms of conditioned fear memory and have led to the identification of the underlying processes involved in fear memory regulation, including cellular and systems consolidation of fear conditioning, destabilization/reconsolidation and extinction after fear memory retrieval, and forgetting of fear memory. These studies suggested that mechanisms for fear memory regulation are shared by humans and other higher animals. Additionally, rodent studies have identified the mechanisms of fear memory at the molecular, cellular, and circuit levels. Findings from these studies in rodents have been applied to facilitate the development and improvement of PTSD intervention. For instance, reconsolidation and extinction of fear memories have been applied for PTSD treatment to improve prolonged exposure (PE) therapy, an effective psychotherapy for PTSD. Combination of medications weakening retrieved traumatic memory (e.g., by facilitating both destabilization and extinction) with PE therapy may contribute to improvement of PTSD. Interestingly, a recent study in mice identified forgetting of fear memory as another potential therapeutic target for PTSD. A better understanding of the mechanisms involved in fear memory processes is likely to facilitate the development of better treatments for PTSD. This review describes fear memory processes and their mechanisms and discusses the pros and cons of applying how this knowledge can be applied in the development of interventions for PTSD.
Keywords: Consolidation; Destabilization; Extinction; Fear memory; Forgetting; PTSD; Reconsolidation.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Behavioral interventions to eliminate fear responses.Sci China Life Sci. 2018 Jun;61(6):625-632. doi: 10.1007/s11427-018-9294-4. Epub 2018 May 7. Sci China Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29744783 Review.
-
Noradrenergic enhancement of reconsolidation in the amygdala impairs extinction of conditioned fear in rats--a possible mechanism for the persistence of traumatic memories in PTSD.Depress Anxiety. 2011 Mar;28(3):186-93. doi: 10.1002/da.20803. Depress Anxiety. 2011. PMID: 21394851 Free PMC article.
-
Fear extinction and memory reconsolidation as critical components in behavioral treatment for posttraumatic stress disorder and potential augmentation of these processes.Neurosci Lett. 2017 May 10;649:170-175. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.01.006. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Neurosci Lett. 2017. PMID: 28065842 Review.
-
[Mechanisms of reconsolidation and extinction of fear memory].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2009 Jun;29(3):125-33. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19663263 Review. Japanese.
-
Function and mechanisms of memory destabilization and reconsolidation after retrieval.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2020;96(3):95-106. doi: 10.2183/pjab.96.008. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32161213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PDE4B Missense Variant Increases Susceptibility to Post-traumatic Stress Disorder-Relevant Phenotypes in Mice.J Neurosci. 2024 Oct 23;44(43):e0137242024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0137-24.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39256048 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Psychological Interventions for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Treatment with Memory Influencing Drugs.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(3):687-707. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666221207162750. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36503450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-acquisition CO2 Inhalation Enhances Fear Memory and Depends on ASIC1A.Front Behav Neurosci. 2021 Oct 29;15:767426. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.767426. eCollection 2021. Front Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34776896 Free PMC article.
-
Post-traumatic stress disorder: the role of the amygdala and potential therapeutic interventions - a review.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 6;15:1356563. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1356563. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38903645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Cannabis on PTSD Recovery: Review of the Literature and Clinical Insights.Curr Addict Rep. 2022 Sep;9(3):203-216. doi: 10.1007/s40429-022-00414-x. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Curr Addict Rep. 2022. PMID: 36385902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abel T, Lattal KM. Molecular mechanisms of memory acquisition, consolidation and retrieval. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2001;11:180–187. - PubMed
-
- Akers KG, Martinez-Canabal A, Restivo L, Yiu AP, De Cristofaro A, Hsiang HL, Wheeler AL, Guskjolen A, Niibori Y, Shoji H, Ohira K, Richards BA, Miyakawa T, Josselyn SA, Frankland PW. Hippocampal neurogenesis regulates forgetting during adulthood and infancy. Science. 2014;344:598–602. - PubMed
-
- Ben Mamou C, Gamache K, Nader K. NMDA receptors are critical for unleashing consolidated auditory fear memories. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:1237–1239. - PubMed
-
- Bentz D, Michael T, de Quervain DJ, Wilhelm FH. Enhancing exposure therapy for anxiety disorders with glucocorticoids: from basic mechanisms of emotional learning to clinical applications. J Anxiety Disord. 2010;24:223–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 15H02488, 18H03944, 23300120, 20380078, 24650172, 26640014, 17K19464, 24116008, 24116001, 23115716, 17H06084, 17H05961, 17H05581, 18H05428, 18022038, 22022039/KAKENHI
- -/Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology
- -/The Science Research Promotion Fund, The Promotion and Mutual Aid Corporation for Private Schools of Japan
- -/Sumitomo Foundation
- -/Naito Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

