Non-catalytic signaling by pseudokinase ILK for regulating cell adhesion
- PMID: 30367047
- PMCID: PMC6203859
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06906-7
Non-catalytic signaling by pseudokinase ILK for regulating cell adhesion
Abstract
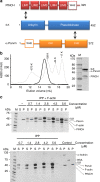
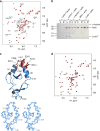
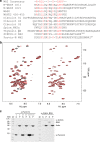
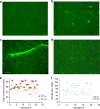
Dynamic communication between integrin-containing complexes (focal adhesions, FAs) and actin filaments is critical for regulating cell adhesion. Pseudokinase ILK plays a key role in this process but the underlying mechanism remains highly elusive. Here we show that by recruiting FA adaptors PINCH and Parvin into a heterotrimeric complex (IPP), ILK triggers F-actin filament bundling - a process known to generate force/mechanical signal to promote cytoskeleton reassembly and dynamic cell adhesion. Structural, biochemical, and functional analyses revealed that the F-actin bundling is orchestrated by two previously unrecognized WASP-Homology-2 actin binding motifs within IPP, one from PINCH and the other from Parvin. Strikingly, this process is also sensitized to Mg-ATP bound to the pseudoactive site of ILK and its dysregulation severely impairs stress fibers formation, cell spreading, and migration. These data identify a crucial mechanism for ILK, highlighting its uniqueness as a pseudokinase to transduce non-catalytic signal and regulate cell adhesion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complex structures of Rsu1 and PINCH1 reveal a regulatory mechanism of the ILK/PINCH/Parvin complex for F-actin dynamics.Elife. 2021 Feb 15;10:e64395. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64395. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33587032 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of pseudokinase ILK-mediated actin assembly.Methods Enzymol. 2022;667:123-146. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2022.03.027. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Methods Enzymol. 2022. PMID: 35525540
-
Molecular dissection of the ILK-PINCH-parvin triad reveals a fundamental role for the ILK kinase domain in the late stages of focal-adhesion maturation.J Cell Sci. 2009 Jun 1;122(Pt 11):1800-11. doi: 10.1242/jcs.044602. Epub 2009 May 12. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19435803
-
The PINCH-ILK-parvin complexes: assembly, functions and regulation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Jul 5;1692(2-3):55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.01.006. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15246679 Review.
-
ILK: a pseudokinase with a unique function in the integrin-actin linkage.Biochem Soc Trans. 2013 Aug;41(4):995-1001. doi: 10.1042/BST20130062. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013. PMID: 23863169 Review.
Cited by
-
Prospects for pharmacological targeting of pseudokinases.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019 Jul;18(7):501-526. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0018-3. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019. PMID: 30850748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tripeptides as Integrin-Linked Kinase Modulating Agents Based on a Protein-Protein Interaction with α-Parvin.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2021 Jul 15;12(11):1656-1662. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.1c00183. eCollection 2021 Nov 11. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 34790291 Free PMC article.
-
A Potential Role for Integrin-Linked Kinase in Colorectal Cancer Growth and Progression via Regulating Senescence and Immunity.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 7;12:638558. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.638558. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34163519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrin-based adhesion compartmentalizes ALK3 of the BMPRII to control cell adhesion and migration.J Cell Biol. 2022 Dec 5;221(12):e202107110. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202107110. Epub 2022 Oct 7. J Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 36205720 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin-linked kinase regulates melanosome trafficking and melanin transfer in melanocytes.Mol Biol Cell. 2020 Apr 1;31(8):768-781. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E19-09-0510. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32049584 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

