Influence of membrane lipid composition on the structure and activity of γ-secretase
- PMID: 30357233
- PMCID: PMC11260083
- DOI: 10.1039/c8cp04138e
Influence of membrane lipid composition on the structure and activity of γ-secretase
Abstract
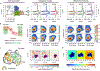
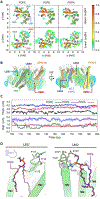
γ-Secretase (GS) is a multi-subunit membrane-embedded aspartyl protease that cleaves more than 80 integral membrane proteins, including the amyloid precursor protein (APP) to produce the amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide. Oligomerization and aggregation of the 42-amino acid length Aβ isoform in the brain has been associated with the development and progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Based on recent experimental structural studies and using multiscale computational modeling approaches, the conformational states and protein-membrane interactions of the GS complex embedded in six homogeneous and six heterogeneous lipid bilayers were characterized. In order to identify potential lipid and cholesterol binding sites, GS regions with high lipid/cholesterol occupancy values were analyzed using atomistic and coarse-grained simulations. Long lipid residence times were observed to be correlated with a large number of hydrogen bonds between the charged headgroups and key GS amino acids. This observation provides a plausible explanation for the inhibition of GS by charged lipids observed in previous experimental studies. Computed lateral pressure profiles suggest that higher transmembrane pressures favor active state conformations of the catalytic subunit. A probable mechanism for the regulation of the local stress response in cholesterol-rich multicomponent lipid bilayers is identified. Finally, it is demonstrated that interactions between the nicastrin extracellular domain and lipid headgroups leads to a compact structural conformation of the GS complex. Overall, this study provides valuable insight into the effect of bilayer lipid composition on the GS structural ensemble and its function.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
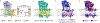
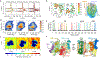
Similar articles
-
Effects of membrane lipids on the activity and processivity of purified γ-secretase.Biochemistry. 2012 May 1;51(17):3565-75. doi: 10.1021/bi300303g. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22489600 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of membrane lipid composition on the structure and stability of the transmembrane domain of amyloid precursor protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Sep 6;113(36):E5281-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1606482113. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27559086 Free PMC article.
-
Active site geometry stabilization of a presenilin homolog by the lipid bilayer promotes intramembrane proteolysis.Elife. 2022 May 17;11:e76090. doi: 10.7554/eLife.76090. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35579427 Free PMC article.
-
Development and mechanism of γ-secretase modulators for Alzheimer's disease.Biochemistry. 2013 May 14;52(19):3197-216. doi: 10.1021/bi400377p. Epub 2013 May 2. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23614767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward the structure of presenilin/γ-secretase and presenilin homologs.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1828(12):2886-97. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.04.015. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 24099007 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A multi-omics investigation of the composition and function of extracellular vesicles along the temporal trajectory of COVID-19.Nat Metab. 2021 Jul;3(7):909-922. doi: 10.1038/s42255-021-00425-4. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Nat Metab. 2021. PMID: 34158670
-
The Role of Cholesterol in Amyloidogenic Substrate Binding to the γ-Secretase Complex.Biomolecules. 2021 Jun 24;11(7):935. doi: 10.3390/biom11070935. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34202467 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and dynamics of γ-secretase with presenilin 2 compared to presenilin 1.RSC Adv. 2019 Jul 4;9(36):20901-20916. doi: 10.1039/c9ra02623a. eCollection 2019 Jul 1. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35515530 Free PMC article.
-
The Binding of Different Substrate Molecules at the Docking Site and the Active Site of γ-Secretase Can Trigger Toxic Events in Sporadic and Familial Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 17;24(3):1835. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031835. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768156 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol and Lipid Rafts in the Biogenesis of Amyloid-β Protein and Alzheimer's Disease.Annu Rev Biophys. 2024 Jul;53(1):455-486. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-062823-023436. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Annu Rev Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38382114 Review.
References
-
- Cai H, Wang Y, McCarthy D, Wen H, Borchelt DR, Price DL and Wong PC, Nat. Neurosci, 2001, 4, 233–234. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

