Extracellular Vesicles From the Dermatophyte Trichophyton interdigitale Modulate Macrophage and Keratinocyte Functions
- PMID: 30356863
- PMCID: PMC6190888
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02343
Extracellular Vesicles From the Dermatophyte Trichophyton interdigitale Modulate Macrophage and Keratinocyte Functions
Abstract
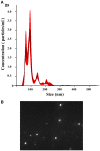
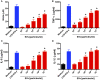
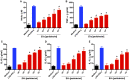
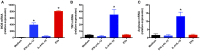
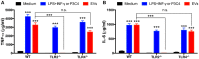
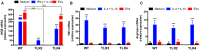
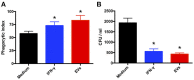
The release of biomolecules critically affects all pathogens and their establishment of diseases. For the export of several biomolecules in diverse species, the use of extracellular vesicles (EVs) is considered to represent an alternative transport mechanism, but no study to date has investigated EVs from dermatophytes. Here, we describe biologically active EVs from the dermatophyte Trichophyton interdigitale, a causative agent of mycoses worldwide. EV preparations from T. interdigitale were examined using nanoparticle-tracking analysis, which revealed vesicular structures 20-380 nm in diameter. These vesicles induced the production of proinflammatory mediators by bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) and keratinocytes in a dose-dependent manner, and an addition of the EVs to BMDMs also stimulated the transcription of the M1-polarization marker iNOS (inducible nitric oxide synthase) and diminished the expression of the M2 markers arginase-1 and Ym-1. The observed M1 macrophages' polarization triggered by EVs was abolished in cells obtained from knockout Toll-like receptor-2 mice. Also, the EVs-induced productions of pro-inflammatory mediators were blocked too. Furthermore, the EVs from T. interdigitale enhanced the fungicidal activity of BMDMs. These results suggest that EVs from T. interdigitale can modulate the innate immune response of the host and influence the interaction between T. interdigitale and host immune cells. Our findings thus open new areas of investigation into the host-parasite relationship in dermatophytosis.
Keywords: Trichophyton interdigitale; extracellular vesicles; fungal infection; innate immunity; keratinocytes; macrophages; nanoparticle-tracking analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicles from Aspergillus flavus Induce M1 Polarization In Vitro.mSphere. 2020 May 6;5(3):e00190-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00190-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32376699 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles from Paracoccidioides brasiliensis induced M1 polarization in vitro.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 24;6:35867. doi: 10.1038/srep35867. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27775058 Free PMC article.
-
Parasite worm antigens instruct macrophages to release immunoregulatory extracellular vesicles.J Extracell Vesicles. 2021 Aug;10(10):e12131. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12131. Epub 2021 Aug 16. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021. PMID: 34429858 Free PMC article.
-
Forkhead Box O1 Regulates Macrophage Polarization Following Staphylococcus aureus Infection: Experimental Murine Data and Review of the Literature.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016 Dec;51(3):353-369. doi: 10.1007/s12016-016-8531-1. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26924010 Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles Deliver Host and Virus RNA and Regulate Innate Immune Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Mar 20;18(3):666. doi: 10.3390/ijms18030666. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28335522 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SUR7 deletion in Candida albicans impacts extracellular vesicle features and delivery of virulence factors.J Extracell Biol. 2023 May 2;2(5):e82. doi: 10.1002/jex2.82. eCollection 2023 May. J Extracell Biol. 2023. PMID: 38938278 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellularly Released Molecules by the Multidrug-Resistant Fungal Pathogens Belonging to the Scedosporium Genus: An Overview Focused on Their Ecological Significance and Pathogenic Relevance.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Nov 7;8(11):1172. doi: 10.3390/jof8111172. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36354939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass Spectrometry Analysis Reveals Lipids Induced by Oxidative Stress in Candida albicans Extracellular Vesicles.Microorganisms. 2023 Jun 27;11(7):1669. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071669. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37512842 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles from Aspergillus flavus Induce M1 Polarization In Vitro.mSphere. 2020 May 6;5(3):e00190-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00190-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32376699 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Cryptococcal Extracellular Vesicles: Experimental Approaches for Studying Their Diversity Among Multiple Isolates, Kinetics of Production, Methods of Separation, and Detection in Cultures of Titan Cells.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Sep 3;9(1):e0012521. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00125-21. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34346749 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

