The affinity, intrinsic activity and selectivity of a structurally novel EP2 receptor agonist at human prostanoid receptors
- PMID: 30341781
- PMCID: PMC6365485
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14525
The affinity, intrinsic activity and selectivity of a structurally novel EP2 receptor agonist at human prostanoid receptors
Abstract
Background and purpose: Prostanoid EP2 receptor agonists exhibit several activities including ocular hypotension, tocolysis and anti-inflammatory activity. This report describes the affinity and selectivity of a structurally novel, non-prostanoid EP2 receptor agonist, PGN-9856, and its therapeutic potential.
Experimental approach: The pharmacology of a series of non-prostanoid EP2 receptor agonists was determined according to functional and radioligand binding studies, mostly using human recombinant prostanoid receptor transfectants. The selectivity of PGN-9856, as the preferred compound, was subsequently determined by using a diverse variety of non-prostanoid target proteins. The therapeutic potential of PGN-9856 was addressed by determining its activity in relevant primate cell, tissue and disease models.
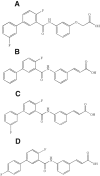
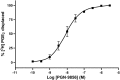
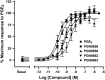
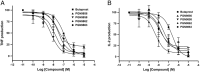
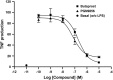
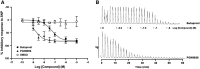
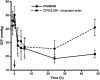
Key results: PGN-9856 was a selective and high affinity (pKi ≥ 8.3) ligand at human recombinant EP2 receptors. In addition to high affinity binding, it was a potent and full EP2 receptor agonist with a high level of selectivity at EP1 , EP3 , EP4 , DP, FP, IP and TP receptors. In cells overexpressing human recombinant EP2 receptors, PGN-9856 displayed a potency (pEC50 ≥ 8.5) and a maximal response (increase in cAMP) comparable to that of the endogenous agonist PGE2 . PGN-9856 exhibited no appreciable affinity (up 10 μM) for a range of 53 other receptors, ion channels and enzymes. Finally, PGN-9856 exhibited tocolytic, anti-inflammatory and long-acting ocular hypotensive properties consistent with its potent EP2 receptor agonist properties.
Conclusions and implications: PGN-9856 is a potent, selective and efficacious prostanoid EP2 receptor agonist with diverse potential therapeutic applications: tocolytic, anti-inflammatory and notably anti-glaucoma.
© 2018 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of the prostanoid receptor(s) on human blood monocytes at which prostaglandin E2 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced tumour necrosis factor-alpha generation.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Sep;122(1):149-57. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701360. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9298541 Free PMC article.
-
Intraocular pressure effects of selective prostanoid receptor agonists involve different receptor subtypes according to radioligand binding studies.J Lipid Mediat. 1993 Mar-Apr;6(1-3):545-53. J Lipid Mediat. 1993. PMID: 8358015
-
In vitro characterization of prostanoid receptors on human myometrium at term pregnancy.Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):501-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12832.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1993. PMID: 8448599 Free PMC article.
-
G protein-coupled prostanoid receptors and the kidney.Annu Rev Physiol. 2001;63:579-605. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.63.1.579. Annu Rev Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11181968 Review.
-
[Cooperation of two subtypes of PGE2 receptor, Gi coupled EP3 and Gs coupled EP2 or EP4 subtype].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003 Oct;123(10):837-43. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.123.837. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 14577329 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Agonism of Prostaglandin E2 Receptor 4 Ameliorates Tubulointerstitial Injury in Nephrotoxic Serum Nephritis in Mice.J Clin Med. 2021 Feb 18;10(4):832. doi: 10.3390/jcm10040832. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33670614 Free PMC article.
-
The role of EP2 receptors in mediating the ultra-long-lasting intraocular pressure reduction by JV-GL1.Br J Ophthalmol. 2021 Nov;105(11):1610-1616. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2020-317762. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Br J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33239414 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive internalisation of EP2 differentially regulates G protein signalling.J Mol Endocrinol. 2024 May 15;73(1):e230153. doi: 10.1530/JME-23-0153. Print 2024 Jul 1. J Mol Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38639976 Free PMC article.
-
Drug discovery strategies for the identification of novel regulators of uterine contractility.Curr Opin Physiol. 2020 Feb;13:71-86. doi: 10.1016/j.cophys.2019.10.012. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Curr Opin Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32864532 Free PMC article.
-
Functional rewiring of G protein-coupled receptor signaling in human labor.Cell Rep. 2022 Sep 6;40(10):111318. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111318. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36070698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramovitz M, Adam M, Boie Y, Carriére M, Denis D et al (2000). The utilization of recombinant prostanoid receptors to determine the affinities and selectivities of prostaglandins and related analogs. Biochim Biophys Acta 1483: 285–293. - PubMed
-
- Aihara M, Lu F, Kawata H, Tanaka Y, Yamamura K et al (2017). Pharmacokinetics, safety and IOP lowering profiles of omidenepag isopropyl, a selective EP2 agonist in healthy Japanese and Caucasian volunteers (phase 1 study). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 58: 2104.
-
- Beck G, Bottomley G, Bradshaw D, Brewster M, Broadhurst M, Devos R et al (2002). (E)‐2(R)‐[1(S)‐(Hydroxycarbamoyl)‐4‐phenyl‐3‐butenyl]‐2′‐isobutyl‐2′‐(methanesulfonyl)‐4‐methylvalerohydrazide (Ro 32‐7315), a selective and orally active inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor‐alpha convertase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302: 390–396. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

