Protective role of down-regulated microRNA-31 on intestinal barrier dysfunction through inhibition of NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway by binding to HMOX1 in rats with sepsis
- PMID: 30340459
- PMCID: PMC6194748
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-018-0053-2
Protective role of down-regulated microRNA-31 on intestinal barrier dysfunction through inhibition of NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway by binding to HMOX1 in rats with sepsis
Abstract
Background: Intestinal barrier dysfunction is a significant clinical problem, commonly developing in a variety of acute or chronic pathological conditions. Herein, we evaluate the effect of microRNA-31 (miR-31) on intestinal barrier dysfunction through NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway by targeting HMOX1 in rats with sepsis.
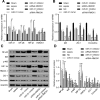
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were collected and divided into the sham group, and the cecum ligation and perforation group which was subdivided after CACO-2 cell transfection of different mimic, inhibitor, or siRNA. Levels of serum D-lactic acid, diamine oxidase and fluorescence isothiocyanate dextran, FITC-DX concentration, and bacterial translocation were detected. Superoxidedismutase (SOD) activity and malondialdehyde (MDA) content were evaluated using the colorimetric method and an automatic microplate reader, respectively. Additionally, the levels of tumor necrosis factor, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-10 were tested using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The expression of miR-31, HMOX1, NF-κB, HIF-1α, IκB, ZO-1 and Occludin were assessed by reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction and Western blot analysis.
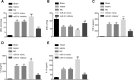
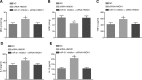
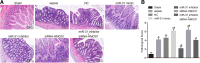
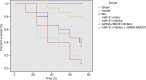
Results: Inhibition of miR-31 decreased intestinal mucosal permeability and intestinal barrier function. The increased levels of miR-31 could cause oxidative damage and affect the expression of inflammatory factors in intestinal tissue of rats. HMOX1 was confirmed as a target gene of miR-31. MiR-31 affected intestinal mucosal permeability and intestinal barrier function, as well as oxidative damage and inflammation level by regulating HMOX1. Down-regulation of miR-31 inhibited NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway related genes by regulating HMOX1 expression. Furthermore, inhibition of miR-31 increased survival rates of rats.
Conclusion: Overall, the current study found that inhibition of miR-31 protects against intestinal barrier dysfunction through suppression of the NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway by targeting HMOX1 in rats with sepsis.
Keywords: HMOX1; Intestinal barrier dysfunction; NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway; Sepsis; microRNA-31.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experimental procedures and the use of animals were approved by the ethics committee on animal experimentation of Tongji Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College of Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication was obtained from the participants.
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
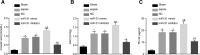

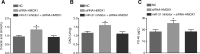
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of miR-155 alleviates sepsis-induced inflammation and intestinal barrier dysfunction by inactivating NF-κB signaling.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Jan;90:107218. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107218. Epub 2020 Dec 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33296782
-
Amelioration of hypoxia and LPS-induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction by emodin through the suppression of the NF-κB and HIF-1α signaling pathways.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Dec;34(6):1629-39. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1965. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 25318952
-
[Protective effects of microRNA-181b on aged rats with sepsis-induced hippocampus injury in vivo].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Jul;31(7):857-861. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.07.012. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 31441410 Chinese.
-
Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):1939-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23770291 Review.
-
Unraveling the role of HIF-1α in sepsis: from pathophysiology to potential therapeutics-a narrative review.Crit Care. 2024 Mar 27;28(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13054-024-04885-4. Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 38539163 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ghrelin/GHSR Axis Induced M2 Macrophage and Alleviated Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in a Sepsis Rat Model by Inactivating E2F1/NF-κB Signaling.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Dec 29;2023:1629777. doi: 10.1155/2023/1629777. eCollection 2023. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 38187112 Free PMC article.
-
The Protective Effects of Protease Inhibitor MG-132 on Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Rats and Its Possible Mechanisms.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Aug 1;25:5690-5699. doi: 10.12659/MSM.915743. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31366881 Free PMC article.
-
Decrease of miR-19b-3p in Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Attenuates Meningitic Escherichia coli-Induced Neuroinflammation via TNFAIP3-Mediated NF-κB Inhibition.Pathogens. 2019 Nov 27;8(4):268. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8040268. Pathogens. 2019. PMID: 31783671 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Ameliorates Liver Injury and Hypoxic Hepatitis in Rat Model of CLP-Induced Sepsis.Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Oct;64(10):2867-2877. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05628-0. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Dig Dis Sci. 2019. PMID: 31049763
-
CB2R agonist GW405833 alleviates acute liver failure in mice via inhibiting HIF-1α-mediated reprogramming of glycometabolism and macrophage proliferation.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023 Jul;44(7):1391-1403. doi: 10.1038/s41401-022-01037-8. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023. PMID: 36697976 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

