Unraveling the Connection between Fibroblast Growth Factor and Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling
- PMID: 30340367
- PMCID: PMC6214098
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19103220
Unraveling the Connection between Fibroblast Growth Factor and Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling
Abstract
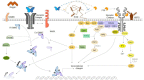
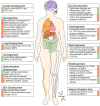
Ontogeny of higher organisms as well the regulation of tissue homeostasis in adult individuals requires a fine-balanced interplay of regulating factors that individually trigger the fate of particular cells to either stay undifferentiated or to differentiate towards distinct tissue specific lineages. In some cases, these factors act synergistically to promote certain cellular responses, whereas in other tissues the same factors antagonize each other. However, the molecular basis of this obvious dual signaling activity is still only poorly understood. Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) and fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) are two major signal protein families that have a lot in common: They are both highly preserved between different species, involved in essential cellular functions, and their ligands vastly outnumber their receptors, making extensive signal regulation necessary. In this review we discuss where and how BMP and FGF signaling cross paths. The compiled data reflect that both factors synchronously act in many tissues, and that antagonism and synergism both exist in a context-dependent manner. Therefore, by challenging a generalization of the connection between these two pathways a new chapter in BMP FGF signaling research will be introduced.
Keywords: bone morphogenetic protein; cross-talk; fibroblast growth factor; signal integration; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Region- and stage-specific effects of FGFs and BMPs in chick mandibular morphogenesis.Dev Dyn. 2002 Mar;223(3):333-52. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.10056. Dev Dyn. 2002. PMID: 11891984
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
-
Requirement for BMP and FGF signaling during cardiogenic induction in non-precardiac mesoderm is specific, transient, and cooperative.Dev Dyn. 2000 Jun;218(2):383-93. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(200006)218:2<383::AID-DVDY11>3.0.CO;2-P. Dev Dyn. 2000. PMID: 10842364
-
Fgf signaling induces posterior neuroectoderm independently of Bmp signaling inhibition.Dev Dyn. 2004 Dec;231(4):750-7. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20244. Dev Dyn. 2004. PMID: 15532058
-
Bone mineralization is regulated by signaling cross talk between molecular factors of local and systemic origin: the role of fibroblast growth factor 23.Biofactors. 2014 Nov-Dec;40(6):555-68. doi: 10.1002/biof.1186. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Biofactors. 2014. PMID: 25352227 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential gene expression in skin RNA of horses affected with degenerative suspensory ligament desmitis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Oct 7;15(1):460. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01994-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 33028365 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the Potential of Stem Cell Microenvironments In Vitro.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Mar 19;11(3):289. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11030289. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FGF signaling in cranial suture development and related diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jun 1;11:1112890. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1112890. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37325554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct Osteogenic Potentials of BMP-2 and FGF-2 in Extramedullary and Medullary Microenvironments.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 27;21(21):7967. doi: 10.3390/ijms21217967. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33120952 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into bone morphogenetic proteins in cardiovascular diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 23;14:1125642. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1125642. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36909186 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

