Regulation of actin-based apical structures on epithelial cells
- PMID: 30333133
- PMCID: PMC6215389
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.221853
Regulation of actin-based apical structures on epithelial cells
Abstract
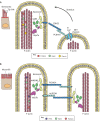
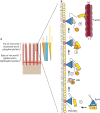
Cells of transporting epithelia are characterized by the presence of abundant F-actin-based microvilli on their apical surfaces. Likewise, auditory hair cells have highly reproducible rows of apical stereocilia (giant microvilli) that convert mechanical sound into an electrical signal. Analysis of mutations in deaf patients has highlighted the critical components of tip links between stereocilia, and related structures that contribute to the organization of microvilli on epithelial cells have been found. Ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) proteins, which are activated by phosphorylation, provide a critical link between the plasma membrane and underlying actin cytoskeleton in surface structures. Here, we outline recent insights into how microvilli and stereocilia are built, and the roles of tip links. Furthermore, we highlight how ezrin is locally regulated by phosphorylation, and that this is necessary to maintain polarity. Localized phosphorylation is achieved through an intricate coincidence detection mechanism that requires the membrane lipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PI(4,5)P2] and the apically localized ezrin kinase, lymphocyte-oriented kinase (LOK, also known as STK10) or Ste20-like kinase (SLK). We also discuss how ezrin-binding scaffolding proteins regulate microvilli and how, despite these significant advances, it remains to be discovered how the cell polarity program ultimately interfaces with these processes.
Keywords: Actin; Cell polarity; Cytoskeleton; ERM proteins; Microvilli; Stereocilia.
© 2018. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure, regulation, and functional diversity of microvilli on the apical domain of epithelial cells.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2015;31:593-621. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100814-125234. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26566117 Review.
-
Effector-mediated ERM activation locally inhibits RhoA activity to shape the apical cell domain.J Cell Biol. 2021 Jun 7;220(6):e202007146. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202007146. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33836044 Free PMC article.
-
Ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM)-binding phosphoprotein 50 organizes ERM proteins at the apical membrane of polarized epithelia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Dec 21;101(51):17705-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407974101. Epub 2004 Dec 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15591354 Free PMC article.
-
Local phosphocycling mediated by LOK/SLK restricts ezrin function to the apical aspect of epithelial cells.J Cell Biol. 2012 Dec 10;199(6):969-84. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201207047. Epub 2012 Dec 3. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23209304 Free PMC article.
-
ERM proteins and NF2 tumor suppressor: the Yin and Yang of cortical actin organization and cell growth signaling.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002 Feb;14(1):104-9. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(01)00300-3. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11792551 Review.
Cited by
-
C-terminal phosphorylation modulates ERM-1 localization and dynamics to control cortical actin organization and support lumen formation during Caenorhabditiselegans development.Development. 2020 Jul 22;147(14):dev188011. doi: 10.1242/dev.188011. Development. 2020. PMID: 32586975 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological Roles of Actin-Binding Scaffold Protein, Ezrin.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 17;23(6):3246. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063246. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tuning of Mechanical Properties in Photopolymerizable Gelatin-Based Hydrogels for In Vitro Cell Culture Systems.ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2023 Jan 27;5(2):1487-1498. doi: 10.1021/acsapm.2c01980. eCollection 2023 Feb 10. ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2023. PMID: 36817339 Free PMC article.
-
Apical-basal polarity and the control of epithelial form and function.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Aug;23(8):559-577. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00465-y. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35440694 Review.
-
The formin inhibitor SMIFH2 inhibits members of the myosin superfamily.J Cell Sci. 2021 Apr 15;134(8):jcs253708. doi: 10.1242/jcs.253708. Epub 2021 Apr 27. J Cell Sci. 2021. PMID: 33589498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avenarius M. R., Krey J. F., Dumont R. A., Morgan C. P., Benson C. B., Vijayakumar S., Cunningham C. L., Scheffer D. I., Corey D. P., Müller U. et al. (2017). Heterodimeric capping protein is required for stereocilia length and width regulation. J. Cell Biol. 216, 3861-3881. 10.1083/jcb.201704171 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

