Canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling pathways define the expression domains of Frizzled 5/8 and Frizzled 1/2/7 along the early anterior-posterior axis in sea urchin embryos
- PMID: 30332609
- PMCID: PMC7920490
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.003
Canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling pathways define the expression domains of Frizzled 5/8 and Frizzled 1/2/7 along the early anterior-posterior axis in sea urchin embryos
Abstract
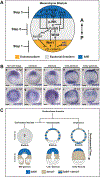
The spatiotemporal expression of Frizzled receptors is critical for patterning along the early anterior-posterior axis during embryonic development in many animal species. However, the molecular mechanisms that regulate the expression of Frizzled receptors are incompletely understood in any species. In this study, I examine how the expression of two Frizzled receptors, Fzl1/2/7 and Fzl5/8, is controlled by the Wnt signaling network which directs specification and positioning of early regulatory states along the anterior-posterior (AP) axis of sea urchin embryos. I used a combination of morpholino- and dominant negative-mediated interference to knock down each Wnt signaling pathway involved in the AP Wnt signaling network. I found that the expression of zygotic fzl5/8 as well as that of the anterior neuroectoderm gene regulatory network (ANE GRN) is activated by an unknown broadly expressed regulatory state and that posterior Wnt/β-catenin signaling is necessary to down regulate fzl5/8's expression in posterior blastomeres. I show that zygotic expression of fzl1/2/7 in the equatorial ectodermal belt is dependent on an uncharacterized regulatory mechanism that works in the same cells receiving the TGF-β signals patterning this territory along the dorsal-ventral axis. In addition, my data indicate that Fzl1/2/7 signaling represses its own expression in a negative feedback mechanism. Finally, we discovered that a balance between the activities of posterior Wnt8 and anterior Dkk1 is necessary to establish the correct spatial expression of zygotic fzl12/7 expression in the equatorial ectodermal domain during blastula and gastrula stages. Together, these studies lead to a better understanding of the complex interactions among the three Wnt signaling pathway governing AP axis specification and patterning in sea urchin embryos.
Keywords: Anterior-posterior; Deuterostome evolution; Fzl1/2/7; Fzl5/8; Gene regulatory networks; Wnt signal transduction.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A biphasic role of non-canonical Wnt16 signaling during early anterior-posterior patterning and morphogenesis of the sea urchin embryo.Development. 2019 Dec 16;146(24):dev168799. doi: 10.1242/dev.168799. Development. 2019. PMID: 31822478 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of canonical and noncanonical Wnt signaling pathways patterns the neuroectoderm along the anterior-posterior axis of sea urchin embryos.PLoS Biol. 2013;11(1):e1001467. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001467. Epub 2013 Jan 15. PLoS Biol. 2013. PMID: 23335859 Free PMC article.
-
A novel gene's role in an ancient mechanism: secreted Frizzled-related protein 1 is a critical component in the anterior-posterior Wnt signaling network that governs the establishment of the anterior neuroectoderm in sea urchin embryos.Evodevo. 2018 Jan 22;9:1. doi: 10.1186/s13227-017-0089-3. eCollection 2018. Evodevo. 2018. PMID: 29387332 Free PMC article.
-
Specification and positioning of the anterior neuroectoderm in deuterostome embryos.Genesis. 2014 Mar;52(3):222-34. doi: 10.1002/dvg.22759. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Genesis. 2014. PMID: 24549984 Review.
-
Heads or tails? Amphioxus and the evolution of anterior-posterior patterning in deuterostomes.Dev Biol. 2002 Jan 15;241(2):209-28. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2001.0503. Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 11784106 Review.
Cited by
-
microRNA-31 regulates skeletogenesis by direct suppression of Eve and Wnt1.Dev Biol. 2021 Apr;472:98-114. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2021.01.008. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33484703 Free PMC article.
-
Echinobase: a resource to support the echinoderm research community.Genetics. 2024 May 7;227(1):iyae002. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae002. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 38262680 Free PMC article.
-
CRYAB promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow stem cells via stabilizing β-catenin and promoting the Wnt signalling.Cell Prolif. 2020 Jan;53(1):e12709. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12709. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 31638302 Free PMC article.
-
A biphasic role of non-canonical Wnt16 signaling during early anterior-posterior patterning and morphogenesis of the sea urchin embryo.Development. 2019 Dec 16;146(24):dev168799. doi: 10.1242/dev.168799. Development. 2019. PMID: 31822478 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases ror1/2 and ryk Are Co-expressed with Multiple Wnt Signaling Components During Early Development of Sea Urchin Embryos.Biol Bull. 2021 Oct;241(2):140-157. doi: 10.1086/715237. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Biol Bull. 2021. PMID: 34706206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Croce J, Duloquin L, Lhomond G, McClay DR, Gache C, 2006. Frizzled5/8 is required in secondary mesenchyme cells to initiate archenteron invagination during sea urchin development. Development 133, 547–557. - PubMed
-
- Darras S, Fritzenwanker JH, Uhlinger KR, Farrelly E, Pani AM, Hurley IA, Norris RP, Osovitz M, Terasaki M, Wu M, Aronowicz J, Kirschner M, Gerhart JC, Lowe CJ, 2018. Anteroposterior axis patterning by early canonical Wnt signaling during hemichordate development. PLoS Biol. 16, e2003698. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

