Antimicrobial activity of certain bacteria and fungi isolated from soil mixed with human saliva against pathogenic microbes causing dermatological diseases
- PMID: 30323712
- PMCID: PMC6181150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2010.06.003
Antimicrobial activity of certain bacteria and fungi isolated from soil mixed with human saliva against pathogenic microbes causing dermatological diseases
Abstract
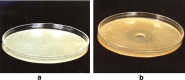
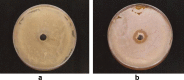
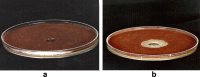
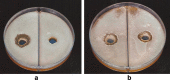
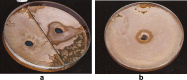
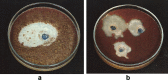
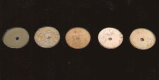
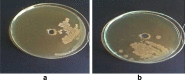
Soil samples (collected from El-Madina El-Monawara, Kingdom Saudi Arabia) were mixed with human saliva, incubated in media suitable for bacterial and fungal growth and filtered. Eighteen bacterial and five fungal species were isolated and identified. The bacterial and fungal filtrates as well as the isolated species were evaluated for their antimicrobial activities against some pathogenic microbes causing dermatological diseases (Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and Aspergillus niger). The bacterial filtrate showed significant antagonistic effect against S. aureus and methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA), whereas showed non inhibitory action on the pathogenic fungus. In contrast, the fungal filtrate antagonized the growth of the pathogenic fungus (A. niger) and did not produce any inhibitory effect on the two tested pathogenic bacteria. The isolated bacterial species showed different levels of antagonistic activities against the three tested microbes. Bacillus subtilis was described as potent isolate against the three pathogens, followed by Esherichia coli. However, Bacillus megaterium strongly inhibited the growth of the pathogenic bacteria only. On the other side, all the fungal filtrates of the isolated species, except Cochliobolus lanatus showed antagonistic activity against the pathogenic fungus (A. niger). The filtrate of Fusarium oxysporum and Emericella nidulans counteracted the growth of S. aureus, whereas, the growth of MRSA was inhibited only by the filtrate of E. nidulans. From the passage way of our respected prophet, how is never tells from him self, if any person complains from awound or ulcer, the messenger of Allah (prayers and peace be upon him) put his forefinger on the ground and lift it then he says: (In the Name of God, soil of our land, with the saliva of some of us, our sick person will get well after the permission of our God) Al-Bukhari. The meaning of this Hadith that the prophet takes his saliva on the forefinger then he put it on the soil and wipe on the wound place while saying the above Hadith that is shows the Prophet's miracle, which is evidence of healing by using soil and saliva.
Keywords: Antimicrobial activity; Aspergillus niger; MRSA; Pathogenic microbes; Saliva; Soil microorganisms; Staphylococcus aureus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Isolation and Characterization of Antagonist Trichoderma spp. from the Soil of Abha, Saudi Arabia.Molecules. 2022 Apr 14;27(8):2525. doi: 10.3390/molecules27082525. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35458723 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic profiling, antimicrobial, anticancer, and in vitro and in silico immunomodulatory investigation of Aspergillus niger OR730979 isolated from the Western Desert, Egypt.Int Microbiol. 2024 Mar 20. doi: 10.1007/s10123-024-00503-z. Online ahead of print. Int Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38506948
-
Biological activities and variation of symbiotic fungi isolated from Coral reefs collected from Red Sea in Egypt.Mycology. 2020 Apr 1;11(3):243-255. doi: 10.1080/21501203.2020.1741470. Mycology. 2020. PMID: 33062385 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive metabolites of Streptomyces misakiensis display broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria and fungi.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Apr 24;13:1162721. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1162721. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37168394 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonistic and antimicrobial activities of some bacterial isolates collected from soil samples.Indian J Microbiol. 2007 Mar;47(1):77-80. doi: 10.1007/s12088-007-0014-x. Epub 2007 Jun 14. Indian J Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 23100644 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Precision drug design against Acidovorax oryzae: leveraging bioinformatics to combat rice brown stripe disease.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Oct 11;13:1225285. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1225285. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37886665 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Novel antimicrobials and antibiotics resistance modulating agents from natural products: Turning promises into Triumphs.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 11;14:1184071. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1184071. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37113752 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Isolation, characterization, and molecular identification of soil bacteria showing antibacterial activity against human pathogenic bacteria.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2021 Aug 18;19(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s43141-021-00219-x. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34406527 Free PMC article.
-
C-protein α-antigen modulates the lantibiotic thusin resistance in Streptococcus agalactiae.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2021 Oct;114(10):1595-1607. doi: 10.1007/s10482-021-01626-3. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2021. PMID: 34319449
-
Autochthonous Enterococcus durans PFMI565 and Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis BGBU1-4 in Bio-Control of Listeria monocytogenes in Ultrafiltered Cheese.Foods. 2021 Jun 22;10(7):1448. doi: 10.3390/foods10071448. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34206521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu Arkoub M.M. The Academic Library; Cairo, Egypt: 2002. Antibiotics and Three Resistors.
-
- Ahmed, A.A., 2003. Biological Study on Some Actinomycetes Isolates. PhD. Thesis. Faculty of Science, AL Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt.
-
- Alexander, M., 1982. Soil Microbiology, second ed. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York.
-
- Aunpad, R., Na-Bangchang, K., 2007. A novel antimicrobial peptide with anti-MRSA activity. 17th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Disease ICC, Munich, Germany.
-
- Barakate M., Ouhdouch Y., Oufdou K.H., Beaulieu C. Characterization of rhizospheric soil streptomycetes from Moroccan habitats and their antimicrobial activities. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002;18(1):49–54.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

