Emodin Sensitizes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to the Anti-Cancer Effect of Sorafenib through Suppression of Cholesterol Metabolism
- PMID: 30321984
- PMCID: PMC6213641
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19103127
Emodin Sensitizes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to the Anti-Cancer Effect of Sorafenib through Suppression of Cholesterol Metabolism
Abstract
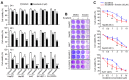
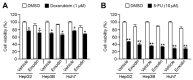
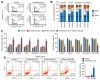
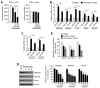
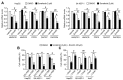
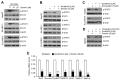
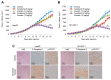
Reduced therapeutic efficacy of sorafenib, a first-generation multikinase inhibitor, is often observed during the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Emodin is an active component of Chinese herbs, and is effective against leukemia, lung cancer, colon cancer, pancreatic cancer, and HCC; however, the sensitizing effect of emodin on sorafenib-based HCC therapy has not been evaluated. Here, we demonstrate that emodin significantly improved the anti-cancer effect of sorafenib in HCC cells, such as HepG2, Hep3B, Huh7, SK-HEP-1, and PLC/PRF5. Mechanistically, emodin inhibits sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 (SREBP-2) transcriptional activity, which suppresses cholesterol biosynthesis and oncogenic protein kinase B (AKT) signaling. Additionally, attenuated cholesterol synthesis and oncogenic AKT signaling inactivated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), an oncogenic transcription factor. Furthermore, emodin synergistically increased cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase and apoptotic cells in the presence of sorafenib. Animal models xenografted with HepG2 or SK-HEP-1 cells also showed that the combination of emodin and sorafenib was sufficient to inhibit tumor growth. Overall, these results suggested that the combination of emodin and sorafenib may offer a potential therapy for patients with advanced HCC.
Keywords: cholesterol; combination; emodin; hepatocellular carcinoma; sorafenib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Capsaicin and sorafenib combination treatment exerts synergistic anti‑hepatocellular carcinoma activity by suppressing EGFR and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling.Oncol Rep. 2018 Dec;40(6):3235-3248. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6754. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30272354 Free PMC article.
-
PMPCB Silencing Sensitizes HCC Tumor Cells to Sorafenib Therapy.Mol Ther. 2019 Oct 2;27(10):1784-1795. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.06.014. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Mol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31337603 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Discovery of Niclosamide Ethanolamine, a Repurposed Drug Candidate That Reduces Growth of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells In Vitro and in Mice by Inhibiting Cell Division Cycle 37 Signaling.Gastroenterology. 2017 Jun;152(8):2022-2036. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.02.039. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Gastroenterology. 2017. PMID: 28284560 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution in medicinal chemistry of sorafenib derivatives for hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Oct 1;179:916-935. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.06.070. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31306818 Review.
-
Capsaicin: Effects on the Pathogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Molecules. 2019 Jun 26;24(13):2350. doi: 10.3390/molecules24132350. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31247901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Maprotiline Suppresses Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression Through Direct Targeting of CRABP1.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 20;12:689767. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.689767. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34093212 Free PMC article.
-
The versatile emodin: A natural easily acquired anthraquinone possesses promising anticancer properties against a variety of cancers.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 May 16;18(8):3498-3527. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.70447. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35637953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combinatorial treatment with traditional medicinal preparations and VEGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors for middle-advanced primary liver cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 22;19(11):e0313443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313443. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39576764 Free PMC article.
-
IDH1R132H Causes Resistance to HDAC Inhibitors by Increasing NANOG in Glioblastoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 31;20(11):2679. doi: 10.3390/ijms20112679. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31151327 Free PMC article.
-
Oridonin Sensitizes Hepatocellular Carcinoma to the Anticancer Effect of Sorafenib by Targeting the Akt Pathway.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Sep 7;12:8081-8091. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S257482. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32982405 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

