Effective detection of biocatalysts with specified activity by using a hydrogel-based colourimetric assay - β-galactosidase case study
- PMID: 30308030
- PMCID: PMC6181394
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205532
Effective detection of biocatalysts with specified activity by using a hydrogel-based colourimetric assay - β-galactosidase case study
Abstract
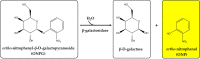
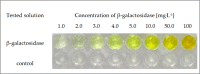
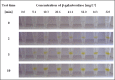
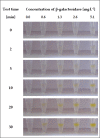
The main aim of this study was to prepare gelatine-based hydrogels containing entrapped substrate and to examine the applicability of these matrices for detection of enzymes with a specified catalytic activity. The general research concept assumed the use of a substrate that, in the presence of a particular enzyme, will quickly undergo conversion to a coloured product. ortho-Nitrophenyl-β-D-galactopyranoside (ONPG) was used as the immobilized substrate and β-galactosidase from Kluyveromyces lactis as the biocatalyst to be determined. Among other factors, the range of detectable concentrations of galactosidase, the operational pH range, the time necessary to achieve a visible response and the preferred storage conditions for the test were determined. As a result, an effective colourimetric test for β-galactosidase detection was obtained. Its main advantages include (i) the effective detection of the enzyme at concentrations greater than or equal to 0.6 mg.L-1, (ii) the ability to perform initial quantification of the enzyme on the basis of the intensity of the obtained colour (iii) applicability in a wide pH range (from 4.0 to 9.0), (iv) a relatively short response time (from 1 to a maximum of 30 minutes) and (v) stability in long-term storage at 4°C (90 days without loss of specific properties).
Conflict of interest statement
The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
β-Galactosidase from Kluyveromyces lactis: Characterization, production, immobilization and applications - A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Nov 30;191:881-898. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.133. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34571129 Review.
-
Lactose hydrolysis using β-galactosidase from Kluyveromyces lactis immobilized with sodium alginate for potential industrial applications.Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2021;51(7):714-722. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2020.1853157. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33287624
-
The β-galactosidase immobilization protocol determines its performance as catalysts in the kinetically controlled synthesis of lactulose.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Apr 15;176:468-478. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.02.078. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33592268
-
High stability of immobilized β-D-galactosidase for lactose hydrolysis and galactooligosaccharides synthesis.Carbohydr Polym. 2013 Jun 5;95(1):465-70. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.02.044. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Carbohydr Polym. 2013. PMID: 23618294
-
Immobilization of β-d-galactosidase from Kluyveromyces lactis on functionalized silicon dioxide nanoparticles: characterization and lactose hydrolysis.Int J Biol Macromol. 2012 Mar 1;50(2):432-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2011.12.029. Epub 2012 Jan 2. Int J Biol Macromol. 2012. PMID: 22230612
Cited by
-
NDM-1 Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae are Highly Susceptible to Ceragenins CSA-13, CSA-44, and CSA-131.Infect Drug Resist. 2020 Sep 28;13:3277-3294. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S261579. eCollection 2020. Infect Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 33061475 Free PMC article.
-
Colourimetric Plate Assays Based on Functionalized Gelatine Hydrogel Useful for Various Screening Purposes in Enzymology.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 20;24(1):33. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010033. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mathur AM, Moorjani SK, Scranton AB. Methods for Synthesis of Hydrogel Networks: A Review. J Macromol Sci Part C Polym Rev. 1996;36: 405–430. 10.1080/15321799608015226 - DOI
-
- Lin C, Gitsov I. Synthesis and physical properties of reactive amphiphilic hydrogels based on poly(p-chloromethylstyrene) and poly (ethylene glycol): Effects of composition and molecular architecture. Macromolecules. 2010;43: 3256–3267. 10.1021/ma9026564 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

