The mitochondrial unfolded protein response and mitohormesis: a perspective on metabolic diseases
- PMID: 30307158
- PMCID: PMC6145237
- DOI: 10.1530/JME-18-0005
The mitochondrial unfolded protein response and mitohormesis: a perspective on metabolic diseases
Abstract
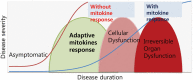
Mitochondria perform essential roles as crucial organelles for cellular and systemic energy homeostasis, and as signaling hubs, which coordinate nuclear transcriptional responses to the intra- and extra-cellular environment. Complex human diseases, including diabetes, obesity, fatty liver disease and aging-related degenerative diseases are associated with alterations in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OxPhos) function. However, a recent series of studies in animal models have revealed that an integrated response to tolerable mitochondrial stress appears to render cells less susceptible to subsequent aging processes and metabolic stresses, which is a key feature of mitohormesis. The mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) is a central part of the mitohormetic response and is a retrograde signaling pathway, which utilizes the mitochondria-to-nucleus communication network. Our understanding of the UPRmt has contributed to elucidating the role of mitochondria in metabolic adaptation and lifespan regulation. In this review, we discuss and integrate recent data from the literature on the present status of mitochondrial OxPhos function in the development of metabolic diseases, relying on evidence from human and other animal studies, which points to alterations in mitochondrial function as a key factor in the regulation of metabolic diseases and conclude with a discussion on the specific roles of UPRmt and mitohormesis as a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of obesity and insulin resistance.
Keywords: mitochondria; oxidative phosphorylation; mitochondrial unfolded protein response; diabetes; insulin resistance.
© 2018 The authors 2018
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of this review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Implications of Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response and Mitokines: A Perspective on Fatty Liver Diseases.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2019 Mar;34(1):39-46. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2019.34.1.39. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2019. PMID: 30912337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795
-
Mitochondrial stress: a bridge between mitochondrial dysfunction and metabolic diseases?Cell Signal. 2011 Oct;23(10):1528-33. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.05.008. Epub 2011 May 15. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 21616143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GDF15 as a central mediator for integrated stress response and a promising therapeutic molecule for metabolic disorders and NASH.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2021 Mar;1865(3):129834. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2020.129834. Epub 2020 Dec 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2021. PMID: 33358864 Review.
-
Evaluating and responding to mitochondrial dysfunction: the mitochondrial unfolded-protein response and beyond.Trends Cell Biol. 2013 Jul;23(7):311-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.02.002. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Trends Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23489877 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biliverdin Reductase-A integrates insulin signaling with mitochondrial metabolism through phosphorylation of GSK3β.Redox Biol. 2024 Jul;73:103221. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103221. Epub 2024 Jun 1. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38843768 Free PMC article.
-
Polydatin and Nicotinamide Rescue the Cellular Phenotype of Mitochondrial Diseases by Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response (mtUPR) Activation.Biomolecules. 2024 May 18;14(5):598. doi: 10.3390/biom14050598. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38786005 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial Effects of Low-Grade Mitochondrial Stress on Metabolic Diseases and Aging.Yonsei Med J. 2024 Feb;65(2):55-69. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2023.0131. Yonsei Med J. 2024. PMID: 38288646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant mitochondrial aggregation of TDP-43 activated mitochondrial unfolded protein response and contributed to recovery of acetaminophen induced acute liver injury.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Jan 25;13(1):tfae008. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae008. eCollection 2024 Feb. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 38283824
-
Emerging roles of mitochondrial functions and epigenetic changes in the modulation of stem cell fate.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jan 12;81(1):26. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-05070-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38212548 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

