Legionella remodels the plasma membrane-derived vacuole by utilizing exocyst components as tethers
- PMID: 30275106
- PMCID: PMC6219717
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201801208
Legionella remodels the plasma membrane-derived vacuole by utilizing exocyst components as tethers
Abstract
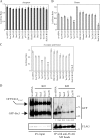
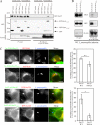
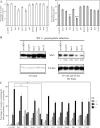
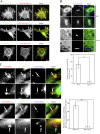
During the initial stage of infection, Legionella pneumophila secretes effectors that promote the fusion of endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-derived vesicles with the Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV). This fusion leads to a remodeling of the plasma membrane (PM)-derived LCV into a specialized ER-like compartment that supports bacterial replication. Although the effector DrrA has been shown to activate the small GTPase Rab1, it remains unclear how DrrA promotes the tethering of host vesicles with the LCV. Here, we show that Sec5, Sec15, and perhaps Sec6, which are subunits of the exocyst that functions in the tethering of exocytic vesicles with the PM, are required for DrrA-mediated, ER-derived vesicle recruitment to the PM-derived LCV. These exocyst components were found to interact specifically with a complex containing DrrA, and the loss of Sec5 or Sec15 significantly suppressed the recruitment of ER-derived vesicles to the LCV and inhibited intracellular replication of Legionella Importantly, Sec15 is recruited to the LCV, and Rab1 activation is necessary for this recruitment.
© 2018 Arasaki et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The machinery at endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane contact sites contributes to spatial regulation of multiple Legionella effector proteins.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Jul 3;10(7):e1004222. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004222. eCollection 2014 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24992562 Free PMC article.
-
AMPylation is critical for Rab1 localization to vacuoles containing Legionella pneumophila.mBio. 2014 Feb 11;5(1):e01035-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01035-13. mBio. 2014. PMID: 24520063 Free PMC article.
-
Legionella hijacks the host Golgi-to-ER retrograde pathway for the association of Legionella-containing vacuole with the ER.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Mar 24;17(3):e1009437. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009437. eCollection 2021 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33760868 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoinositides and the Fate of Legionella in Phagocytes.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 30;11:25. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00025. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32117224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution and function of bacterial RCC1 repeat effectors.Cell Microbiol. 2020 Oct;22(10):e13246. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13246. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Cell Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32720355 Review.
Cited by
-
In through the Out Exit: the Role of the Exocyst in Listeria monocytogenes Cell Entry.Infect Immun. 2022 Dec 15;90(12):e0048422. doi: 10.1128/iai.00484-22. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Infect Immun. 2022. PMID: 36394320 Free PMC article.
-
Using proteomics to identify host cell interaction partners for VgrG and IglJ.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 3;10(1):14612. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71641-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32884055 Free PMC article.
-
Pushing boundaries: mechanisms enabling bacterial pathogens to spread between cells.Infect Immun. 2024 Sep 10;92(9):e0052423. doi: 10.1128/iai.00524-23. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Infect Immun. 2024. PMID: 38661369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shigella hijacks the exocyst to cluster macropinosomes for efficient vacuolar escape.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Aug 31;16(8):e1008822. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008822. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32866204 Free PMC article.
-
Host Lipid Manipulation by Intracellular Bacteria: Moonlighting for Immune Evasion.J Membr Biol. 2023 Dec;256(4-6):393-411. doi: 10.1007/s00232-023-00296-8. Epub 2023 Nov 8. J Membr Biol. 2023. PMID: 37938349 Review.
References
-
- Bodemann B.O., Orvedahl A., Cheng T., Ram R.R., Ou Y.H., Formstecher E., Maiti M., Hazelett C.C., Wauson E.M., Balakireva M., et al. . 2011. RalB and the exocyst mediate the cellular starvation response by direct activation of autophagosome assembly. Cell. 144:253–267. 10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brombacher E., Urwyler S., Ragaz C., Weber S.S., Kami K., Overduin M., and Hilbi H.. 2009. Rab1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor SidM is a major phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate-binding effector protein of Legionella pneumophila. J. Biol. Chem. 284:4846–4856. 10.1074/jbc.M807505200 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

