Downregulation of CD147 induces malignant melanoma cell apoptosis via the regulation of IGFBP2 expression
- PMID: 30272281
- PMCID: PMC6203154
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4579
Downregulation of CD147 induces malignant melanoma cell apoptosis via the regulation of IGFBP2 expression
Erratum in
-
[Corrigendum] Downregulation of CD147 induces malignant melanoma cell apoptosis via the regulation of IGFBP2 expression.Int J Oncol. 2024 Jan;64(1):3. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5591. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 37997849 Free PMC article.
Abstract
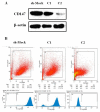
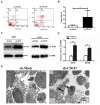
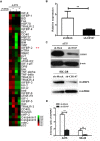
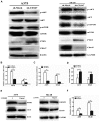
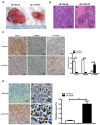
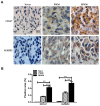
Cluster of differentiation (CD)147, as a transmembrane glycoprotein, is highly expressed in a variety of tumors. Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that CD147 serves critical roles in tumor cell death and survival; however, the underlying mechanism requires further investigation. In the present study, it was revealed that CD147 knockdown significantly increased melanoma cell apoptosis. In addition, downregulation of CD147 reversed the malignant phenotype of melanoma, as demonstrated by the induction of tumor cell apoptosis in a xenograft mouse model. In addition, a human apoptosis antibody array was performed and 9 differentially expressed apoptosis-related proteins associated with CD147 were identified, including insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 (IGFBP2). Additionally, CD147 knockdown was observed to significantly decreased IGFBP2 expression at the mRNA and protein levels in melanoma cells. Providing that IGFBP2 is a downstream molecule in the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)/phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway, the effects of CD147 on this particular pathway were investigated. Interestingly, the expression of phosphorylated (p)-AKT and p‑mechanistic target of rapamycin was attenuated, whereas PTEN was markedly upregulated in CD147-underexpressing melanoma cells. Furthermore, application of a PI3K‑specific inhibitor also decreased IGFBP2 expression. Importantly, IGFBP2 was highly expressed in clinical tissues of melanoma compared with the control group, and its expression exhibited a positive association with CD147. The present study revealed that CD147 served a critical role in mediating the apoptosis of melanoma cells via IGFBP2 and the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. IGFBP2 and CD147 were observed to be overexpressed in clinical melanoma tissues; IGFBP2 was shown to be positively associated with CD147 expression, suggesting that CD147 may be considered as a potential therapeutic target for chemotherapy or prevention for in melanoma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CD147 silencing inhibits tumor growth by suppressing glucose transport in melanoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 4;7(40):64778-64784. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11415. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27556188 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo anti-malignant melanoma activity of Alocasia cucullata via modulation of the phosphatase and tensin homolog/phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Mar 1;213:359-365. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.11.025. Epub 2017 Dec 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29180042
-
The phosphorylation of CD147 by Fyn plays a critical role for melanoma cells growth and metastasis.Oncogene. 2020 May;39(21):4183-4197. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1287-3. Epub 2020 Apr 14. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 32291412
-
Repressing CD147 is a novel therapeutic strategy for malignant melanoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 11;8(15):25806-25813. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15709. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28445958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the PTEN Tumor Suppressor Gene and Its Anti-Angiogenic Activity in Melanoma and Other Cancers.Molecules. 2024 Feb 4;29(3):721. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030721. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Application of Deep Learning in the Risk Grading of Skin Tumors for Patients Using Clinical Images.J Med Syst. 2019 Jul 13;43(8):283. doi: 10.1007/s10916-019-1414-2. J Med Syst. 2019. PMID: 31300897
-
Severe recurrent hypoglycaemia in a patient with aggressive melanoma.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Aug 5;14(8):e243468. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-243468. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34353831 Free PMC article.
-
CD147 Facilitates the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis through Glycolysis and H3K9me3 Modification in Keratinocytes.Research (Wash D C). 2023 Jun 8;6:0167. doi: 10.34133/research.0167. eCollection 2023. Research (Wash D C). 2023. PMID: 37303600 Free PMC article.
-
Large-Scale Single-Cell and Bulk Sequencing Analyses Reveal the Prognostic Value and Immune Aspects of CD147 in Pan-Cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 6;13:810471. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.810471. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35464411 Free PMC article.
-
SETDB1-mediated CD147-K71 di-methylation promotes cell apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer.Genes Dis. 2023 Mar 24;11(2):978-992. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.02.015. eCollection 2024 Mar. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 37692516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold M, Holterhues C, Hollestein LM, Coebergh JW, Nijsten T, Pukkala E, Holleczek B, Tryggvadóttir L, Comber H, Bento MJ, et al. Trends in incidence and predictions of cutaneous melanoma across Europe up to 2015. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:1170–1178. doi: 10.1111/jdv.12236. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

