Epigenetic Enhancer Marks and Transcription Factor Binding Influence Vκ Gene Rearrangement in Pre-B Cells and Pro-B Cells
- PMID: 30271408
- PMCID: PMC6146092
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02074
Epigenetic Enhancer Marks and Transcription Factor Binding Influence Vκ Gene Rearrangement in Pre-B Cells and Pro-B Cells
Abstract
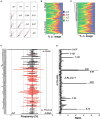
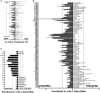
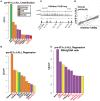
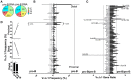
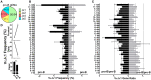
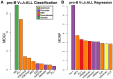
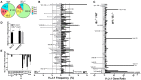
To date there has not been a study directly comparing relative Igκ rearrangement frequencies obtained from genomic DNA (gDNA) and cDNA and since each approach has potential biases, this is an important issue to clarify. Here we used deep sequencing to compare the unbiased gDNA and RNA Igκ repertoire from the same pre-B cell pool. We find that ~20% of Vκ genes have rearrangement frequencies ≥2-fold up or down in RNA vs. DNA libraries, including many members of the Vκ3, Vκ4, and Vκ6 families. Regression analysis indicates Ikaros and E2A binding are associated with strong promoters. Within the pre-B cell repertoire, we observed that individual Vκ genes rearranged at very different frequencies, and also displayed very different Jκ usage. Regression analysis revealed that the greatly unequal Vκ gene rearrangement frequencies are best predicted by epigenetic marks of enhancers. In particular, the levels of newly arising H3K4me1 peaks associated with many Vκ genes in pre-B cells are most predictive of rearrangement levels. Since H3K4me1 is associated with long range chromatin interactions which are created during locus contraction, our data provides mechanistic insight into unequal rearrangement levels. Comparison of Igκ rearrangements occurring in pro-B cells and pre-B cells from the same mice reveal a pro-B cell bias toward usage of Jκ-distal Vκ genes, particularly Vκ10-96 and Vκ1-135. Regression analysis indicates that PU.1 binding is the highest predictor of Vκ gene rearrangement frequency in pro-B cells. Lastly, the repertoires of iEκ-/- pre-B cells reveal that iEκ actively influences Vκ gene usage, particularly Vκ3 family genes, overlapping with a zone of iEκ-regulated germline transcription. These represent new roles for iEκ in addition to its critical function in promoting overall Igκ rearrangement. Together, this study provides insight into many aspects of Igκ repertoire formation.
Keywords: Next Generation Sequencing; V(D)J recombination; enhancer; immunoglobulin; pre-B cells; pro-B cells; repertoire.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamic Control of Long-Range Genomic Interactions at the Immunoglobulin κ Light-Chain Locus.Adv Immunol. 2015;128:183-271. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2015.07.004. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Adv Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26477368 Review.
-
PU.1 Regulates Ig Light Chain Transcription and Rearrangement in Pre-B Cells during B Cell Development.J Immunol. 2017 Feb 15;198(4):1565-1574. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601709. Epub 2017 Jan 6. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28062693
-
Vκ gene repertoire and locus contraction are specified by critical DNase I hypersensitive sites within the Vκ-Jκ intervening region.J Immunol. 2013 Feb 15;190(4):1819-26. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203127. Epub 2013 Jan 7. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23296705 Free PMC article.
-
De novo DNA Methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b regulate the onset of Igκ light chain rearrangement during early B-cell development.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Aug;45(8):2343-55. doi: 10.1002/eji.201445035. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26059604
-
Transcription factories in Igκ allelic choice and diversity.Adv Immunol. 2019;141:33-49. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2018.11.001. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Adv Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30904132 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular basis for differential Igk versus Igh V(D)J joining mechanisms.Nature. 2024 Jun;630(8015):189-197. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07477-y. Epub 2024 May 29. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38811728 Free PMC article.
-
New insights emerge as antibody repertoire diversification meets chromosome conformation.F1000Res. 2019 Mar 28;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-347. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.17358.1. eCollection 2019. F1000Res. 2019. PMID: 30984378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Locus architecture and RAG scanning determine antibody diversity.Trends Immunol. 2023 Feb;44(2):119-128. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2022.12.005. Trends Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36706738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helix-Loop-Helix Proteins in Adaptive Immune Development.Front Immunol. 2022 May 12;13:881656. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.881656. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35634342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EBF1, PAX5, and MYC: regulation on B cell development and association with hematologic neoplasms.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 22;15:1320689. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1320689. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38318177 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Williams GS, Martinez A, Montalbano A, Tang A, Mauhar A, Ogwaro KM, et al. . Unequal VH gene rearrangement frequency within the large VH7183 gene family is not due to RSS variation, and mapping of the genes shows a bias of rearrangement based on chromosomal location. J Immunol. (2001) 167:257–63. 10.4049/jimmunol.167.1.257 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Feeney AJ, Lugo G, Escuro G. Human cord blood k repertoire. J Immunol. (1997) 158:3761–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

