The novel NADPH oxidase 4 selective inhibitor GLX7013114 counteracts human islet cell death in vitro
- PMID: 30265686
- PMCID: PMC6161897
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204271
The novel NADPH oxidase 4 selective inhibitor GLX7013114 counteracts human islet cell death in vitro
Abstract
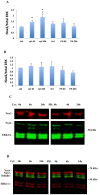
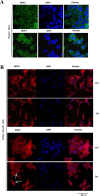
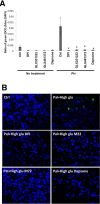
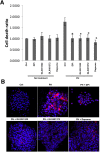
It has been proposed that pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes is promoted by oxidative stress caused by NADPH oxidase (Nox) over-activity. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the efficacy of novel Nox inhibitors as protective agents against cytokine- or high glucose + palmitate-induced human beta-cell death. The Nox2 protein was present mainly in the cytoplasm and was induced by cytokines. Nox4 protein immunoreactivity, with some nuclear accumulation, was observed in human islet cells, and was not affected by islet culture in the presence of cytokines or high glucose + palmitate. Nox inhibitors with partial or no isoform selectivity (DPI, dapsone, GLX351322, and GLX481372) all reduced ROS production of human islet cells exposed to high glucose + palmitate. This was paralleled by improved viability and reduced caspase 3 activation. The Nox1 selective inhibitor ML171 failed to reduce human islet cell death in response to both cytokines and high glucose + palmitate. The selective Nox2 inhibitor Phox-I2 also failed to protect against cytokines, but protected partially against high glucose + palmitate-induced cellular death. The highly selective Nox4 inhibitor GLX7013114 protected islet cells against both cytokines and high glucose + palmitate. However, as no osmotic control for high glucose was used, we cannot exclude the possibility that the high glucose effect was due to osmosis. It is concluded that Nox4 may participate in stress-induced islet cell death in human islets in vitro. We propose that Nox4 mediates pro-apoptotic effects in intact islets under stressful conditions and that selective Nox4-inhibition may be a therapeutic strategy in type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
XW, AE, NW, and P-OC have no conflict of interest to disclose. PW and EW have applied for the following patents: Wilcke M, Walum E, Wikström P. Thiophene-based compounds exhibiting nox4 inhibitory activity and use thereof in therapy. 2013 Patent application number PCT/EP2013/055218, and the European patent application No. 18171556.6 submitted 2018-05-09 protecting the Nox4 selective compound GLX7013114. The funder Glucox Biotech AB provided support in the form of salaries for authors EW and PW. Glucox Biotech AB has supported this study by generating, characterizing and providing NOX inhibitors. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. NOX inhibitors will be shared pending patent publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The novel NADPH oxidase 4 inhibitor GLX351322 counteracts glucose intolerance in high-fat diet-treated C57BL/6 mice.Free Radic Res. 2015;49(11):1308-18. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2015.1067697. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Free Radic Res. 2015. PMID: 26118714
-
Glucose, palmitate and pro-inflammatory cytokines modulate production and activity of a phagocyte-like NADPH oxidase in rat pancreatic islets and a clonal beta cell line.Diabetologia. 2007 Feb;50(2):359-69. doi: 10.1007/s00125-006-0462-6. Epub 2006 Dec 7. Diabetologia. 2007. PMID: 17151863
-
Targeting of NADPH oxidase in vitro and in vivo suppresses fibroblast activation and experimental skin fibrosis.Exp Dermatol. 2017 Jan;26(1):73-81. doi: 10.1111/exd.13180. Exp Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 27576129
-
Potential benefits and harms of NADPH oxidase type 4 in the kidneys and cardiovascular system.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019 Apr 1;34(4):567-576. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfy161. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019. PMID: 29931336 Review.
-
Role of pancreatic beta-cells in the process of beta-cell death.Diabetes. 2001 Feb;50 Suppl 1:S52-7. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.2007.s52. Diabetes. 2001. PMID: 11272203 Review.
Cited by
-
Reactive oxygen species in biological systems: Pathways, associated diseases, and potential inhibitors-A review.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Dec 1;12(2):675-693. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3784. eCollection 2024 Feb. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38370049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-oxidant effect of nitrite in the pancreatic islets of type 2 diabetic male rats.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023 Apr;26(4):420-428. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.68245.14900. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37009002 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Virus-Induced Inflammation in Zebrafish: A Balance Between Infection Control and Excessive Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2021 May 7;12:636623. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636623. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34025644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dapsone, More than an Effective Neuro and Cytoprotective Drug.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(1):194-210. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210617143108. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34139984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevention of Oxidative Stress-Induced Pancreatic Beta Cell Damage by Broussonetia Kazinoki Siebold Fruit Extract Via the ERK-Nox4 Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 May 10;9(5):406. doi: 10.3390/antiox9050406. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32397640 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sakai K, Matsumoto K, Nishikawa T, Suefuji M, Nakamaru K, Hirashima Y, et al. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species reduce insulin secretion by pancreatic beta-cells. Biochemical Biophysical Research Communications. 2003; 300(1): 216–222. - PubMed
-
- Evans JL, Goldfine ID, Maddux BA, Grodsky GM. (2003) Are oxidative stress-activated signaling pathways mediators of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction? Diabetes. 2003; 52(1):1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

