CD36 Promotes Podocyte Apoptosis by Activating the Pyrin Domain-Containing-3 (NLRP3) Inflammasome in Primary Nephrotic Syndrome
- PMID: 30258045
- PMCID: PMC6178869
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.909810
CD36 Promotes Podocyte Apoptosis by Activating the Pyrin Domain-Containing-3 (NLRP3) Inflammasome in Primary Nephrotic Syndrome
Abstract
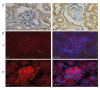
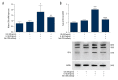
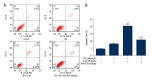
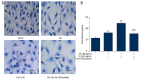
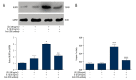
BACKGROUND CD36 plays a critical role in many sterile inflammatory diseases, including type 2 diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, and primary nephrotic syndrome. This study investigated whether CD36 activates the nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat-containing family, pyrin domain-containing-3 (NLRP3) inflammasome and promotes podocytes apoptosis in primary nephrotic syndrome. MATERIAL AND METHODS The mouse podocyte cell line MPC5 was used as a model. mRNA and protein expression of CD36 and NLRP3 was quantified by real-time PCR and Western blotting, respectively. Levels of caspase-1 activity and total cholesterol were determined using commercial kits. Intracellular lipid droplets were detected by Oil Red O staining. CD36 expression was also examined in nephrotic mouse kidney tissue by immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence. Intracellular lipid droplet was examined by Oil Red O staining. RESULTS CD36 expression was increased in nephrotic mouse kidney tissue. Treatment with interleukin-1b increased expression of CD36 and total cholesterol in MPC5 cells. Moreover, this treatment increased expression of NLRP3 and the percentage of apoptotic cells, both of which were inhibited by co-treatment with an anti-CD36 antibody. CONCLUSIONS CD36 might play an important role in podocyte apoptosis by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome in primary nephrotic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CD36-Mediated Lipid Accumulation and Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Lead to Podocyte Injury in Obesity-Related Glomerulopathy.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Apr 11;2019:3172647. doi: 10.1155/2019/3172647. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 31097920 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to aldosterone-induced podocyte injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Apr 1;312(4):F556-F564. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00332.2016. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28052869
-
Interleukin-17A participates in podocyte injury by inducing IL-1β secretion through ROS-NLRP3 inflammasome-caspase-1 pathway.Scand J Immunol. 2018 Apr;87(4):e12645. doi: 10.1111/sji.12645. Epub 2018 Mar 5. Scand J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29446486
-
Regulation and Function of the Nucleotide Binding Domain Leucine-Rich Repeat-Containing Receptor, Pyrin Domain-Containing-3 Inflammasome in Lung Disease.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016 Feb;54(2):151-60. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2015-0231TR. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26418144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative regulators and their mechanisms in NLRP3 inflammasome activation and signaling.Immunol Cell Biol. 2017 Aug;95(7):584-592. doi: 10.1038/icb.2017.23. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Immunol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28356568 Review.
Cited by
-
Podocyte Bioenergetics in the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy: The Role of Mitochondria.Endocrinology. 2022 Jan 1;163(1):bqab234. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab234. Endocrinology. 2022. PMID: 34791124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of the inflammasome and pyroptosis cascade in podocytes of patients with minimal change disease.Clin Kidney J. 2024 Jul 16;17(8):sfae216. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfae216. eCollection 2024 Aug. Clin Kidney J. 2024. PMID: 39114498 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk Between Lipids and Mitochondria in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Curr Diab Rep. 2019 Nov 21;19(12):144. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1263-x. Curr Diab Rep. 2019. PMID: 31754839 Review.
-
The NLRP3 Inflammasome: Metabolic Regulation and Contribution to Inflammaging.Cells. 2020 Jul 30;9(8):1808. doi: 10.3390/cells9081808. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32751530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tripterygium glycosides improve abnormal lipid deposition in nephrotic syndrome rat models.Ren Fail. 2023 Dec;45(1):2182617. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2182617. Ren Fail. 2023. PMID: 36876728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lesley R, Paul AB, Detlef B, Nicholas JA. Pediatric nephrology. 2nd ed. Oxford University Press; UK: 2012.
-
- Kriz W. Podocyte is the major culprit accounting for the progression of chronic renal disease. Microsc Res Tech. 2002;57:189–95. - PubMed
-
- Liu S, Vaziri ND. Role of PCSK9 and IDOL in the pathogenesis of acquired LDL receptor deficiency and hypercholesterolemia in nephrotic syndrome. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 2014;29:538–43. - PubMed
-
- Yang Z, Ming X. CD36: the common soil for inflammation in obesity and atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;89:485–86. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

