The Effects of Ginsenoside Compound K Against Epilepsy by Enhancing the γ-Aminobutyric Acid Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 30254585
- PMCID: PMC6142013
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01020
The Effects of Ginsenoside Compound K Against Epilepsy by Enhancing the γ-Aminobutyric Acid Signaling Pathway
Abstract
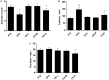
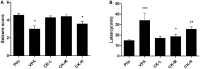
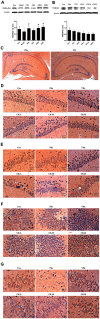
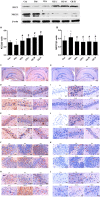
The imbalance between the GABA-mediated inhibition and the glutamate-mediated excitation is the primary pathological mechanism of epilepsy. GABAergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission have become the most important targets for controlling epilepsy. Ginsenoside compound K (GCK) is a main metabolic production of the ginsenoside Rb1, Rb2, and Rc in the intestinal microbiota. Previous studies show that GCK promoted the release of GABA from the hippocampal neurons and enhanced the activity of GABAA receptors. GCK is shown to reduce the expression of NMDAR and to attenuate the function of the NMDA receptors in the brain. The anti-seizure effects of GCK have not been reported so far. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effects of GCK on epilepsy and its potential mechanism. The rat model of seizure or status epilepticus (SE) was established with either Pentylenetetrazole or Lithium chloride-pilocarpine. The Racine's scale was used to evaluate seizure activity. The levels of the amino acid neurotransmitters were detected in the pilocarpine-induced epileptic rats. The expression levels of GABAARα1, NMDAR1, KCC2, and NKCC1 protein in the hippocampus were determined via western blot or immunohistochemistry after SE. We found that GCK had deceased seizure intensity and prolonged the latency of seizures. GCK increased the contents of GABA, while the contents of glutamate remained unchanged. GCK enhanced the expression of GABAARα1 in the brain and exhibited a tendency to decrease the expression of NMDAR1 protein in the hippocampus. The expression of KCC2 protein was elevated by the treatment of GCK after SE, while the expression of NKCC1 protein was reversely down-regulated. These findings suggested that GCK exerted anti-epileptic effects by promoting the hippocampal GABA release and enhancing the GABAAR-mediated inhibitory synaptic transmission.
Keywords: GABAARα1; KCC2; NKCC1; epilepsy; ginsenoside compound K; neurotransmitters.
Figures
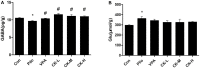
Similar articles
-
Aucubin Alleviates Seizures Activity in Li-Pilocarpine-Induced Epileptic Mice: Involvement of Inhibition of Neuroinflammation and Regulation of Neurotransmission.Neurochem Res. 2019 Feb;44(2):472-484. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2700-y. Epub 2019 Jan 21. Neurochem Res. 2019. PMID: 30666488
-
Seizures regulate the cation-Cl- cotransporter NKCC1 in a hamster model of epilepsy: implications for GABA neurotransmission.Front Neurol. 2023 Jun 22;14:1207616. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1207616. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37448751 Free PMC article.
-
Anomalous levels of Cl- transporters cause a decrease of GABAergic inhibition in human peritumoral epileptic cortex.Epilepsia. 2011 Sep;52(9):1635-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03111.x. Epub 2011 Jun 2. Epilepsia. 2011. PMID: 21635237
-
Early polytherapy for benzodiazepine-refractory status epilepticus.Epilepsy Behav. 2019 Dec;101(Pt B):106367. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.06.011. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Epilepsy Behav. 2019. PMID: 31636007 Review.
-
Role of NKCC1 and KCC2 in Epilepsy: From Expression to Function.Front Neurol. 2020 Jan 17;10:1407. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.01407. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32010056 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A narrative review of the pharmacology of ginsenoside compound K.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Feb;10(4):234. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-501. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35280413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay between microbiota and brain-gut axis in epilepsy treatment.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 26;15:1276551. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1276551. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38344171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Protein-Rich Extract from Bombyx Batryticatus against Glutamate-Damaged PC12 Cells Via Regulating γ-Aminobutyric Acid Signaling Pathway.Molecules. 2020 Jan 28;25(3):553. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030553. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32012896 Free PMC article.
-
A narrative review on traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions and bioactive components in epilepsy treatment.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Jan 31;11(2):129. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3306. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36819494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginsenoside Compound K: Insights into Recent Studies on Pharmacokinetics and Health-Promoting Activities.Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 10;10(7):1028. doi: 10.3390/biom10071028. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32664389 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

