Role of a combination dietary supplement containing mucopolysaccharides, vitamin C, and collagen on tendon healing in rats
- PMID: 30245052
- PMCID: PMC6318503
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aott.2018.06.012
Role of a combination dietary supplement containing mucopolysaccharides, vitamin C, and collagen on tendon healing in rats
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of mucopolysaccharide, vitamin C, and collagen supplementation on the healing of Achilles tendon in rats.
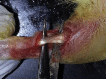
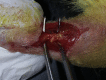
Methods: Sixteen rats were separated into 2 groups. Both Achilles tendons of all rats were transected 5 mm above the insertion and repaired using a Kessler suture. After the surgical repair, the study group received the daily recommended amount of the supplement by gastric gavage, while the control group received a placebo. At the end of the third week, the animals were sacrificed. The biomechanical properties of the groups were compared with ultimate tensile strength and stiffness tests. The biological properties of the 2 groups were assessed with a histomorphometric comparison to determine the amount of collagen type I (COL1), proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) expression in 3 different tissue subgroups (collagen matrix, tenocytes, and endotenon fibroblasts).
Results: Analysis of histomorphometric results revealed that the rats receiving dietary supplements demonstrated a significant increase in PCNA (mean value of 86 in the control group and 168.85 in the trial group; p < 0.05) and TGF-β1 (mean value of 87.57 in the control group and 161.85 in the trial group; p < 0.05) in the endotenon fibroblasts of the repair site. However, there was no difference between the groups in PCNA or TGF-β1 when the collagen matrix and the tenocytes of the repair site were examined. Furthermore, no significant difference could be found between groups in COL1 in any of the 3 tissue subgroups (collagen matrix, tenocytes, and endotenon fibroblasts). The statistical analysis also indicated that the rats receiving supplements did not demonstrate a significant increase in the ultimate tendon tensile strength or stiffness.
Conclusion: The results of this study revealed no advantage to the oral administration of the trial supplement in collagen synthesis or biomechanical properties in rats after 3 weeks using the presented study design. However, the increased expression of PCNA and TGFβ1 seen in the endotenon fibroblasts of the repair site might play a role in the continuum of tendon healing.
Keywords: Collagen; Dietary supplement; Mucopolysaccharides; Tendon healing; Vitamin C.
Copyright © 2018 Turkish Association of Orthopaedics and Traumatology. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



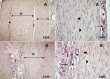
 : Collagen fiber;
: Collagen fiber;  : Tenocyte;
: Tenocyte;  : Blood vessel;
: Blood vessel;  : Fibroblasts; E: Endotendineum; TF: Tendon fascicule.
: Fibroblasts; E: Endotendineum; TF: Tendon fascicule.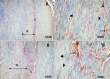
 : Collagen fiber;
: Collagen fiber;  : Tenocyte;
: Tenocyte;  : Blood vessel;
: Blood vessel;  : Fibroblasts. E: Endotendineum.
: Fibroblasts. E: Endotendineum.Similar articles
-
Effect of Vitamin C on Tendinopathy Recovery: A Scoping Review.Nutrients. 2022 Jun 27;14(13):2663. doi: 10.3390/nu14132663. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35807843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracorporeal shock waves promote healing of collagenase-induced Achilles tendinitis and increase TGF-beta1 and IGF-I expression.J Orthop Res. 2004 Jul;22(4):854-61. doi: 10.1016/j.orthres.2003.10.013. J Orthop Res. 2004. PMID: 15183445
-
Transforming growth factor beta 1 mediates the low-frequency vertical vibration enhanced production of tenomodulin and type I collagen in rat Achilles tendon.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 11;13(10):e0205258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205258. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30307981 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on rat Achilles tendon healing.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003 Nov;112(6):1613-9. doi: 10.1097/01.PRS.0000086772.72535.A4. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003. PMID: 14578792
-
Efficacy of Vitamin C Supplementation on Collagen Synthesis and Oxidative Stress After Musculoskeletal Injuries: A Systematic Review.Orthop J Sports Med. 2018 Oct 25;6(10):2325967118804544. doi: 10.1177/2325967118804544. eCollection 2018 Oct. Orthop J Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 30386805 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of C60 Fullerene on Recovery of Muscle Soleus in Rats after Atrophy Induced by Achillotenotomy.Life (Basel). 2022 Feb 23;12(3):332. doi: 10.3390/life12030332. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35330083 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Vitamin C on Tendinopathy Recovery: A Scoping Review.Nutrients. 2022 Jun 27;14(13):2663. doi: 10.3390/nu14132663. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35807843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Regulation of Tendon Inflammation and Healing Following Injury.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021 Feb 10;23(3):15. doi: 10.1007/s11926-021-00981-4. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33569739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ESWT and nutraceutical supplementation (Tendisulfur Forte) vs ESWT-only in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis, Achilles tendinopathy, and rotator cuff tendinopathy: a comparative study.J Drug Assess. 2019 May 3;8(1):77-86. doi: 10.1080/21556660.2019.1605370. eCollection 2019. J Drug Assess. 2019. PMID: 31105990 Free PMC article.
-
Healing Effect of a Nano-Functionalized Medical-Grade Honey for the Treatment of Infected Wounds.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 24;15(9):2187. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092187. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Langberg H., Skovgaard D., Asp S., Kjaer M. Time pattern of exercise-induced changes in type I collagen turnover after prolonged endurance exercise in humans. Calcif Tissue Int. 2000 Jul;67(1):41–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
