Control of DNA Replication Initiation by Ubiquitin
- PMID: 30241373
- PMCID: PMC6211026
- DOI: 10.3390/cells7100146
Control of DNA Replication Initiation by Ubiquitin
Abstract
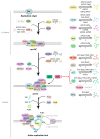
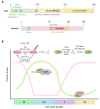
Eukaryotic cells divide by accomplishing a program of events in which the replication of the genome is a fundamental part. To ensure all cells have an accurate copy of the genome, DNA replication occurs only once per cell cycle and is controlled by numerous pathways. A key step in this process is the initiation of DNA replication in which certain regions of DNA are marked as competent to replicate. Moreover, initiation of DNA replication needs to be coordinated with other cell cycle processes. At the molecular level, initiation of DNA replication relies, among other mechanisms, upon post-translational modifications, including the conjugation and hydrolysis of ubiquitin. An example is the precise control of the levels of the DNA replication initiation protein Cdt1 and its inhibitor Geminin by ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation. This control ensures that DNA replication occurs with the right timing during the cell cycle, thereby avoiding re-replication events. Here, we review the events that involve ubiquitin signalling during DNA replication initiation, and how they are linked to human disease.
Keywords: DNA replication Initiation; proteasome; ubiquitin; ubiquitin hydrolases; ubiquitin ligases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
USP37 deubiquitinates Cdt1 and contributes to regulate DNA replication.Mol Oncol. 2016 Oct;10(8):1196-206. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2016.05.008. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Mol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27296872 Free PMC article.
-
Replication-dependent destruction of Cdt1 limits DNA replication to a single round per cell cycle in Xenopus egg extracts.Genes Dev. 2005 Jan 1;19(1):114-26. doi: 10.1101/gad.1255805. Epub 2004 Dec 14. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 15598982 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of DNA Replication Licensing and Re-Replication by Cdt1.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 14;22(10):5195. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105195. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34068957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SCF(Skp2) ubiquitin ligase complex interacts with the human replication licensing factor Cdt1 and regulates Cdt1 degradation.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 15;278(33):30854-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C300251200. Epub 2003 Jul 2. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12840033
-
Cdt1 interactions in the licensing process: a model for dynamic spatiotemporal control of licensing.Cell Cycle. 2007 Jul 1;6(13):1549-52. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.13.4455. Epub 2007 May 22. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17598984 Review.
Cited by
-
CDT1, transcriptionally regulated by E2F2, promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 22;10(16):e36557. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36557. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39262963 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting NPM1 in irradiated cells inhibits NPM1 binding to RAD51, RAD51 foci formation and radiosensitizes NSCLC.Cancer Lett. 2021 Mar 1;500:220-227. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.12.023. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 33358698 Free PMC article.
-
USP7 Is a Master Regulator of Genome Stability.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 5;8:717. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00717. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32850836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The E3 ligase RFWD3 stabilizes ORC in a p53-dependent manner.Cell Cycle. 2020 Nov;19(21):2927-2938. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1829823. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 33044890 Free PMC article.
-
An electroporation cytometry system for long-term, live cell cycle analysis.Biomicrofluidics. 2024 Aug 6;18(4):044105. doi: 10.1063/5.0204837. eCollection 2024 Jul. Biomicrofluidics. 2024. PMID: 39219593
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

