Pembrolizumab and salvage chemotherapy in EGFR T790M-positive non-small-cell lung cancer with high PD-L1 expression
- PMID: 30237726
- PMCID: PMC6135433
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S168598
Pembrolizumab and salvage chemotherapy in EGFR T790M-positive non-small-cell lung cancer with high PD-L1 expression
Abstract
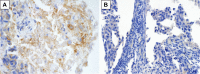
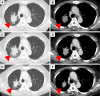
Immuno-checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have become an effective treatment option for non-small-cell lung cancer patients. However, ICI therapy was reported to be less effective in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations than in those with wild-type EGFR. We report here that an non-small-cell lung cancer patient with the EGFR mutant T790M showed a programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression level that increased from <25% to >90% after eighth-line osimertinib therapy. He was treated with pembrolizumab as a ninth-line treatment, and attained stable disease. After the pembrolizumab therapy, he was treated with gemcitabine, which produced a good response despite being the 10th-line treatment. We should consider administering ICI and chemotherapy even to EGFR mutant patients after failure of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, especially in cases with high PD-LI expression.
Keywords: chemotherapy post immunotherapy; epidermal growth factor receptor mutation; lung cancer; programmed cell death ligand 1.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two cases of response to pembrolizumab in epidermal growth factor receptor mutated lung adenocarcinoma patients with programmed death-ligand 1 overexpression.Ann Transl Med. 2018 Nov;6(22):444. doi: 10.21037/atm.2018.10.24. Ann Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30596074 Free PMC article.
-
Association between programmed death-ligand 1 expression, immune microenvironments, and clinical outcomes in epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung adenocarcinoma patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Eur J Cancer. 2020 Jan;124:110-122. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.10.019. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Eur J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31760310
-
PD-L1 expression and response to pembrolizumab in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2020 May 5;50(5):617-622. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyaa033. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32211792
-
It might be a dead end: immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in EGFR-mutated NSCLC.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024;5(4):826-840. doi: 10.37349/etat.2024.00251. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024. PMID: 39280252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway, Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and the Regulation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 5;20(15):3821. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153821. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31387256 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ferumoxytol and CpG oligodeoxynucleotide 2395 synergistically enhance antitumor activity of macrophages against NSCLC with EGFRL858R/T790M mutation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Jun 24;14:4503-4515. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S193583. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31417255 Free PMC article.
-
[Application Progress of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Oncogene-driven Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2021 Mar 20;24(3):188-195. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2021.101.04. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33819969 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 16;12:955440. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.955440. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36052255 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

