Prevalence of Homologous Recombination-Related Gene Mutations Across Multiple Cancer Types
- PMID: 30234181
- PMCID: PMC6139373
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.17.00286
Prevalence of Homologous Recombination-Related Gene Mutations Across Multiple Cancer Types
Abstract
Purpose: The prevalence of homologous recombination DNA damage repair (HR-DDR) deficiencies among all tumor lineages is not well characterized. Therapy directed toward homologous recombination DDR deficiency (HRD) is now approved in ovarian and breast cancer, and there may be additional opportunities for benefit for patients with other cancers. Comprehensive evaluations for HRD are limited in part by the lack of a uniform, cost-effective method for testing and defining HRD.
Methods: Molecular profiles of 52,426 tumors were reviewed to identify pathogenic mutations in the HR-DDR genes ARID1A, ATM, ATRX, BAP1, BARD1, BLM, BRCA1/2, BRIP1, CHEK1/2, FANCA/C/D2/E/F/G/L, MRE11A, NBN, PALB2, RAD50, RAD51, RAD51B, or WRN. From solid tumors submitted to Caris Life Sciences, molecular profiles were generated using next-generation sequencing (NGS; average read depth, 500×). A total of 17,566 tumors were sequenced with NGS600 (n = 592 genes), and 34,860 tumors underwent hotspot Illumina MiSeq platform testing (n = 47 genes).
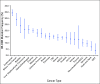
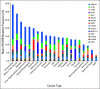
Results: Of the tumors that underwent NGS600 testing, the overall frequency of HRDDR mutations detected was 17.4%, and the most commonly mutated lineages were endometrial (34.4%; n = 1,475), biliary tract (28.9%; n = 343), bladder (23.9%; n = 201), hepatocellular (20.9%; n = 115), gastroesophageal (20.8%; n = 619), and ovarian (20.0%; n = 2,489). Least commonly mutated lineages included GI stromal (3.7%; n = 108), head and neck (6.8%; n = 206), and sarcoma (9.3%; n = 592). ARID1A was the most commonly mutated gene (7.2%), followed by BRCA2 (3.0%), BRCA1 (2.8%), ATM (1.3%), ATRX (1.3%), and CHEK2 (1.3%).
Conclusions: HR-DDR mutations were seen in 17.4% of tumors across 21 cancer lineages, providing a path to explore the role of HRD-directed therapies, including poly-ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors, DNA-damaging chemotherapies, and newer agents such as ATR inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
AUTHORS’ DISCLOSURES OF POTENTIAL CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO’s conflict of interest policy, please refer to www.asco.org/rwc or ascopubs.org/po/author-center. Arielle L. Heeke No relationship to disclose Michael J. Pishvaian Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Perthera Honoraria: Caris Life Sciences, Celgene, Sirtex Medical, Merrimack Consulting or Advisory Role: Caris Life Sciences, Perthera, Celgene, Sirtex Medical, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, RenovoRx Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Caris Life Sciences, Sirtex Medical, Perthera, AstraZeneca/MedImmune Filipa Lynce Joanne Xiu Employment: Caris Life Sciences Jonathan R. Brody Consulting or Advisory Role: Perthera Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Perthera Wang-Juh Chen Employment: Caris Life Sciences Tabari M. Baker Employment: Caris Life Sciences, Roche Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Caris Life Sciences, Roche John L. Marshall Employment: Caris Life Sciences Honoraria: Roche, Amgen, Bayer/Onyx, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Caris Life Sciences, Celgene Consulting or Advisory Role: Roche, Amgen, Bayer/Onyx, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Caris Life Sciences, Celgene Speakers’ Bureau: Roche, Amgen, Bayer/Onyx, Celgene, Taiho Pharmaceutical Claudine Isaacs Honoraria: Roche, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Novartis, Syndax, NanoString Technologies Consulting or Advisory Role: Pfizer, Roche, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Medivation, NanoString Technologies, Syndax Speakers’ Bureau: Genentech, Pfizer, AstraZeneca Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: UpToDate, McGraw Hill Publishing
Figures
Similar articles
-
Actionable co-alterations in breast tumors with pathogenic mutations in the homologous recombination DNA damage repair pathway.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Nov;184(2):265-275. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05849-2. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32776290
-
Next generation sequencing reveals a high prevalence of pathogenic mutations in homologous recombination DNA damage repair genes among patients with uterine sarcoma.Gynecol Oncol. 2023 Oct;177:14-19. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2023.07.020. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Gynecol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37611378
-
Analysis of DNA Damage Response Gene Alterations and Tumor Mutational Burden Across 17,486 Tubular Gastrointestinal Carcinomas: Implications for Therapy.Oncologist. 2019 Oct;24(10):1340-1347. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0034. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 31040255 Free PMC article.
-
Homologous Recombination Deficiency: Cancer Predispositions and Treatment Implications.Oncologist. 2021 Sep;26(9):e1526-e1537. doi: 10.1002/onco.13829. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Oncologist. 2021. PMID: 34021944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recommendations for Preventive Care for Women with Rare Genetic Cause of Breast and Ovarian Cancer.Klin Onkol. 2019 Summer;32(Supplementum2):6-13. doi: 10.14735/amko2019S6. Klin Onkol. 2019. PMID: 31409076 Review. English.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and Prognostic Relevance of Homologous Recombination Repair Gene Mutations in Uterine Serous Carcinoma.Cells. 2022 Nov 11;11(22):3563. doi: 10.3390/cells11223563. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36428992 Free PMC article.
-
A Benchmark of In-House Homologous Recombination Repair Deficiency Testing Solutions for High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Oct 24;13(21):3293. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13213293. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958189 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the genotoxicity of Fusobacterium nucleatum-secreted mutagens in colorectal cancer carcinogenesis.Gut Pathog. 2024 Sep 27;16(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13099-024-00640-w. Gut Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39334474 Free PMC article.
-
The Prognostic and Therapeutic Potential of DNA Damage Repair Pathway Alterations and Homologous Recombination Deficiency in Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 28;14(21):5305. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215305. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATM inhibition enhance immunotherapy by activating STING signaling and augmenting MHC Class I.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jul 20;15(7):519. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06911-3. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39033176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuchenbaecker KB, Hopper JL, Barnes DR, et al. Risks of breast, ovarian, and contralateral breast cancer for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers. JAMA. 2017;317:2402–2416. - PubMed
-
- Mavaddat N, Peock S, Frost D, et al. Cancer risks for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers: Results from prospective analysis of EMBRACE. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105:812–822. - PubMed
-
- van der Kolk DM, de Bock GH, Leegte BK, et al. Penetrance of breast cancer, ovarian cancer and contralateral breast cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 families: High cancer incidence at older age. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;124:643–651. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

