The cell cycle regulatory DREAM complex is disrupted by high expression of oncogenic B-Myb
- PMID: 30206359
- PMCID: PMC6377300
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-018-0490-y
The cell cycle regulatory DREAM complex is disrupted by high expression of oncogenic B-Myb
Abstract
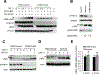
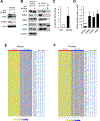
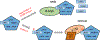
Overexpression of the oncogene MYBL2 (B-Myb) is associated with increased cell proliferation and serves as a marker of poor prognosis in cancer. However, the mechanism by which B-Myb alters the cell cycle is not fully understood. In proliferating cells, B-Myb interacts with the MuvB core complex including LIN9, LIN37, LIN52, RBBP4, and LIN54, forming the MMB (Myb-MuvB) complex, and promotes transcription of genes required for mitosis. Alternatively, the MuvB core interacts with Rb-like protein p130 and E2F4-DP1 to form the DREAM complex that mediates global repression of cell cycle genes in G0/G1, including a subset of MMB target genes. Here, we show that overexpression of B-Myb disrupts the DREAM complex in human cells, and this activity depends on the intact MuvB-binding domain in B-Myb. Furthermore, we found that B-Myb regulates the protein expression levels of the MuvB core subunit LIN52, a key adapter for assembly of both the DREAM and MMB complexes, by a mechanism that requires S28 phosphorylation site in LIN52. Given that high expression of B-Myb correlates with global loss of repression of DREAM target genes in breast and ovarian cancer, our findings offer mechanistic insights for aggressiveness of cancers with MYBL2 amplification, and establish the rationale for targeting B-Myb to restore cell cycle control.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simultaneous expression of MMB-FOXM1 complex components enables efficient bypass of senescence.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 2;11(1):21506. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01012-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34728711 Free PMC article.
-
The MuvB complex sequentially recruits B-Myb and FoxM1 to promote mitotic gene expression.Genes Dev. 2012 Mar 1;26(5):474-89. doi: 10.1101/gad.181933.111. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22391450 Free PMC article.
-
Structural mechanism of Myb-MuvB assembly.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Oct 2;115(40):10016-10021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1808136115. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30224471 Free PMC article.
-
MuvB: A Key to Cell Cycle Control in Ovarian Cancer.Front Oncol. 2018 Jun 11;8:223. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00223. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29942794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell cycle transcription control: DREAM/MuvB and RB-E2F complexes.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Dec;52(6):638-662. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2017.1360836. Epub 2017 Aug 11. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28799433 Review.
Cited by
-
c-Myb promotes growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer through c-fos-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Cancer Sci. 2019 Oct;110(10):3183-3196. doi: 10.1111/cas.14141. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 31338937 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of MuvB complexes.Oncogene. 2022 May;41(21):2909-2919. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02321-x. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35468940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclin F drives proliferation through SCF-dependent degradation of the retinoblastoma-like tumor suppressor p130/RBL2.Elife. 2021 Dec 1;10:e70691. doi: 10.7554/eLife.70691. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34851822 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and Comprehensive Analysis of Underlying microRNA-mRNA Interactive Networks in Ovarian Cancer.J Oncol. 2022 Mar 10;2022:5120342. doi: 10.1155/2022/5120342. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35310909 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupting the DREAM complex enables proliferation of adult human pancreatic β cells.J Clin Invest. 2022 Aug 1;132(15):e157086. doi: 10.1172/JCI157086. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35700053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allegra CJ, Aberle DR, Ganschow P, Hahn SM, Lee CN, Millon-Underwood S et al. National Institutes of Health State-of-the-Science Conference statement: Diagnosis and Management of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ September 22–24, 2009. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2010; 102: 161–169. - PubMed
-
- Becker W, Sippl W. Activation, regulation, and inhibition of DYRK1 A. The FEBS journal 2011; 278: 246–256. - PubMed
-
- Dedic Plavetic N, Jakic-Razumovic J, Kulic A, Vrbanec D. Prognostic value of proliferation markers expression in breast cancer. Medical oncology 2013; 30: 523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

