AKT inhibitor MK-2206 sensitizes breast cancer cells to MLN4924, a first-in-class NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE) inhibitor
- PMID: 30198810
- PMCID: PMC6224269
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1515550
AKT inhibitor MK-2206 sensitizes breast cancer cells to MLN4924, a first-in-class NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE) inhibitor
Abstract
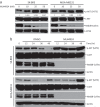
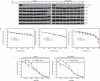
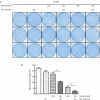
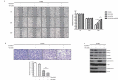
Breast cancer is a common type of cancer among female cancer patients and the main cause of cancer-related deaths. During the last decades, targeted therapies for breast cancer have been rapidly developing. Among them, MLN4924, a first-in-class NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE) inhibitor, has performed antitumor activity by inactivating the cullin-RING ligases and causing the accumulation of their substrates to induce apoptosis in a number of studies. In this study, we found that MLN4924 activates the AKT pathway in both HER2-positive and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell lines. Given that AKT signaling is responsible for tumor progression and drug resistance in some types of cancers, we hypothesized that the AKT inhibitor may synergistically enhance the tumor suppression capability in breast cancer by MLN4924. To demonstrate the sensitizing effect, MK-2206 was chosen as the adjuvant treatment, and cell growth, migration and apoptosis were detected. The results showed that MLN4924 treatment inhibited cell growth and migration and induced apoptosis in both SK-BR3 and MDA-MB231 breast cancer cell lines. More importantly, the combined treatment of MLN4924 and MK-2206 indeed caused stronger cytotoxicity and inhibition of migration and a much higher induction of apoptosis compared with MLN4924 treatment alone. Our study provides the proof-of-concept evidence for strategic drug combination of MLN4924 with an AKT inhibitor for maximal killing of breast cancer cells via the enhancement of apoptosis.
Keywords: AKT inhibitor; Breast cancer; MK-2206; MLN4924; neddylation; targeted therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MLN4924, an NAE inhibitor, suppresses AKT and mTOR signaling via upregulation of REDD1 in human myeloma cells.Blood. 2014 May 22;123(21):3269-76. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-08-521914. Epub 2014 Apr 8. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24713927 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of p21-dependent senescence by an NAE inhibitor, MLN4924, as a mechanism of growth suppression.Neoplasia. 2011 Jun;13(6):561-9. doi: 10.1593/neo.11420. Neoplasia. 2011. PMID: 21677879 Free PMC article.
-
The NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibition with MLN4924 sensitizes human cancer cells of different origins to apoptosis and necroptosis.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Sep 30;691:108513. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108513. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 32721435
-
The Double-Edged Effects of MLN4924: Rethinking Anti-Cancer Drugs Targeting the Neddylation Pathway.Biomolecules. 2024 Jun 21;14(7):738. doi: 10.3390/biom14070738. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MLN4924 therapy as a novel approach in cancer treatment modalities.J Chemother. 2016 Apr;28(2):74-82. doi: 10.1179/1973947815Y.0000000066. J Chemother. 2016. PMID: 26292710 Review.
Cited by
-
ATM inhibitor KU60019 synergistically sensitizes lung cancer cells to topoisomerase II poisons by multiple mechanisms.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 17;13(1):882. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28185-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36650267 Free PMC article.
-
miR‑589‑3p sponged by the lncRNA TINCR inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion and promotes the apoptosis of breast cancer cells by suppressing the Akt pathway via IGF1R.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Sep;46(3):989-1002. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4666. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32705168 Free PMC article.
-
5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine advances the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells by demethylating Sipa1 promoter-proximal elements.J Cell Sci. 2020 May 11;133(9):jcs236125. doi: 10.1242/jcs.236125. J Cell Sci. 2020. PMID: 32193333 Free PMC article.
-
SCFβ-TrCP-mediated degradation of TOP2β promotes cancer cell survival in response to chemotherapeutic drugs targeting topoisomerase II.Oncogenesis. 2020 Feb 3;9(2):8. doi: 10.1038/s41389-020-0196-1. Oncogenesis. 2020. PMID: 32015321 Free PMC article.
-
Protein neddylation and its role in health and diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Apr 5;9(1):85. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01800-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38575611 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A.. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7–30. PMID: 29313949. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Morales-Vasquez F, Hortobagyi GN. Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in patients with breast cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;608:1–22. PMID: 17993229. - PubMed
-
- Robert NJ, Diéras V, Glaspy J, et al. RIBBON-1: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase iii trial of chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for first-line treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative, locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(10):1252–1260. PMID: 21383283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
