Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Specifically Targets Human CD1d Antigen Presentation To Enhance Its Pathogenicity
- PMID: 30185591
- PMCID: PMC6206489
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01490-18
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Specifically Targets Human CD1d Antigen Presentation To Enhance Its Pathogenicity
Abstract
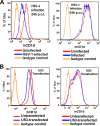
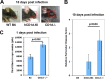
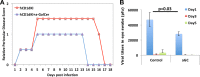
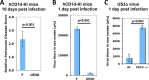
Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) is one of the most prevalent herpesviruses in humans and represents a constant health threat to aged and immunocompromised populations. How HSV-1 interacts with the host immune system to efficiently establish infection and latency is only partially known. CD1d-restricted NKT cells are a critical arm of the host innate immune system and play potent roles in anti-infection and antitumor immune responses. We discovered previously that upon infection, HSV-1 rapidly and efficiently downregulates CD1d expression on the cell surface and suppresses the function of NKT cells. Furthermore, we identified the viral serine/threonine protein kinase US3 as a major viral factor downregulating CD1d during infection. Interestingly, neither HSV-1 nor its US3 protein efficiently inhibits mouse CD1d expression, suggesting that HSV-1 has coevolved with the human immune system to specifically suppress human CD1d (hCD1d) and NKT cell function for its pathogenesis. This is consistent with the fact that wild-type mice are mostly resistant to HSV-1 infection. On the other hand, in vivo infection of CD1d-humanized mice (hCD1d knock-in mice) showed that HSV-1 can indeed evade hCD1d function and establish infection in these mice. We also report here that US3-deficient viruses cannot efficiently infect hCD1d knock-in mice but infect mice lacking all NKT cells at a higher efficiency. Together, these studies supported HSV-1 evasion of human CD1d and NKT cell function as an important pathogenic factor for the virus. Our results also validated the potent roles of NKT cells in antiherpesvirus immune responses and pointed to the potential of NKT cell ligands as adjuvants for future vaccine development.IMPORTANCE Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) is among the most common human pathogens. Little is known regarding the exact mechanism by which this virus evades the human immune system, particularly the innate immune system. We reported previously that HSV-1 employs its protein kinase US3 to modulate the expression of the key antigen-presenting molecule, CD1d, so as to evade the antiviral function of NKT cells. Here we demonstrated that the virus has coevolved with the human CD1d and NKT cell system and that NKT cells indeed play potent roles in anti-HSV immune responses. These studies point to the great potential of exploring NKT cell ligands as adjuvants for HSV vaccines.
Keywords: CD1d; HSV-1; NKT cell; US3; immune evasion; mouse model; pathogenicity.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 US3 Phosphorylates Cellular KIF3A To Downregulate CD1d Expression.J Virol. 2015 Jul;89(13):6646-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00214-15. Epub 2015 Apr 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25878107 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein B and US3 collaborate to inhibit CD1d antigen presentation and NKT cell function.J Virol. 2011 Aug;85(16):8093-104. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02689-10. Epub 2011 Jun 8. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21653669 Free PMC article.
-
A Thr/Ser dual residue motif in the cytoplasmic tail of human CD1d is important for the down-regulation of antigen presentation following a herpes simplex virus 1 infection.Immunology. 2013 Oct;140(2):191-201. doi: 10.1111/imm.12127. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23710894 Free PMC article.
-
[Molecular mechanism by which Us3 protein kinase regulates the pathogenicity of herpes simplex virus type-1].Uirusu. 2016;66(1):83-90. doi: 10.2222/jsv.66.83. Uirusu. 2016. PMID: 28484184 Review. Japanese.
-
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection of Neuronal and Non-Neuronal Cells Elicits Specific Innate Immune Responses and Immune Evasion Mechanisms.Front Immunol. 2021 May 31;12:644664. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.644664. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34135889 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The surveillance of viral infections by the unconventional Type I NKT cell.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 17;15:1472854. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1472854. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39355244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Features of the CD1 gene family in rodents and the uniqueness of the immune system of naked mole-rat.Biol Direct. 2024 Jul 29;19(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13062-024-00503-z. Biol Direct. 2024. PMID: 39075541 Free PMC article.
-
The immune system in neurological diseases: What innate-like T cells have to say.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024 Apr;153(4):913-923. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2024.02.003. Epub 2024 Feb 15. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38365015 Review.
-
Die Kämpfe únd schláchten-the struggles and battles of innate-like effector T lymphocytes with microbes.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 24;14:1117825. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1117825. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37168859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potent NKT cell ligands overcome SARS-CoV-2 immune evasion to mitigate viral pathogenesis in mouse models.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Mar 24;19(3):e1011240. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011240. eCollection 2023 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 36961850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kimberlin DW, Whitley RJ. 2007. Antiviral therapy of HSV-1 and -2. In Arvin A, Campadelli-Fiume G, Mocarski E, Moore PS, Roizman B, Whitley R, Yamanishi K (ed), Human herpesviruses: biology, therapy, and immunoprophylaxis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

