Bacterial Bioprinting on a Flexible Substrate for Fabrication of a Colorimetric Temperature Indicator by Using a Commercial Inkjet Printer
- PMID: 30181965
- PMCID: PMC6116318
- DOI: 10.4103/jmss.JMSS_41_17
Bacterial Bioprinting on a Flexible Substrate for Fabrication of a Colorimetric Temperature Indicator by Using a Commercial Inkjet Printer
Abstract
Background: Bacterial sensors are recommended for medical sciences, pharmaceutical industries, food industries, and environmental monitoring due to low cost, high sensitivity, and appropriate response time. There are some advantages of using bacterial spores instead of bacteria in vegetative forms as spores remain alive without any nutrient for a long time and change to vegetative form when a suitable environment is provided for them.
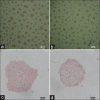
Methods: For biosensor fabrication, it is important to define how the bacterial spores are delivered to the substrate media. The main purpose of this paper is an investigation of transferring bacterial spores on a flexible substrate media using a commercial inkjet printer (HP Deskjet 1510). It should be noted that in the previous researches, the special printers were used to transfer bacteria on rigid films.
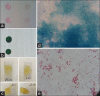
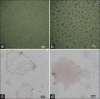
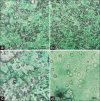
Results: These printed bacterial spores are used as a colorimetric temperature indicator. The custom-made bio-inks are prepared by bacterial spores along with a gelling agent and pH indicator.
Conclusions: Finally, transformation of bacterial spores into vegetative bacteria is occurred by changing of temperature. A color change in the bio-prints is demonstrated because the bacterial transformation and growth change the environmental pH to an acidic level.
Keywords: Bacterial spores; biosensor; colorimetric indicator; flexible substrate; printer.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An inkjet-printed sulfonephthalein dye indicator array for volatile amine detection.J Food Sci. 2020 Feb;85(2):442-454. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15020. Epub 2020 Jan 24. J Food Sci. 2020. PMID: 31976555
-
Inkjet-printed CO2 colorimetric indicators.Talanta. 2016 Dec 1;161:105-113. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2016.08.014. Epub 2016 Aug 20. Talanta. 2016. PMID: 27769385
-
Fabrication of a Silver-Based Thermistor on Flexible, Temperature-Sensitive Substrates Using a Low-Temperature Inkjet Printing Technique.IEEE Sens Lett. 2019 Jan 17;3(2):10.1109/LSENS.2019.2893741. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2019.2893741. IEEE Sens Lett. 2019. PMID: 32083240 Free PMC article.
-
Inkjet printing for biosensor fabrication: combining chemistry and technology for advanced manufacturing.Lab Chip. 2015 Jun 21;15(12):2538-58. doi: 10.1039/c5lc00235d. Lab Chip. 2015. PMID: 25953427 Review.
-
Detection and enumeration of injured bacterial spores in processed foods.Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1984;(12):241-56. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1984. PMID: 6387933 Review.
Cited by
-
3D bioprinting of microorganisms: principles and applications.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2024 Apr;47(4):443-461. doi: 10.1007/s00449-023-02965-3. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2024. PMID: 38296889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D Bioprinting in Tissue Engineering for Medical Applications: The Classic and the Hybrid.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Jul 31;12(8):1717. doi: 10.3390/polym12081717. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32751797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Theoretical and Experimental Assay of Shock Experienced by Yeast Cells during Laser Bioprinting.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;23(17):9823. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179823. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077218 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Developments in 3D Bio-Printing and Its Biomedical Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 11;15(1):255. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010255. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recapitulating Tumorigenesis in vitro: Opportunities and Challenges of 3D Bioprinting.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Jun 22;9:682498. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.682498. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34239860 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aikio S, Grnqvist S, Hakola L, Hurme E. Bioactive Paper and Fibre Products VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland. 2006:83.
-
- Lukacs G, Maloney N, Hegner M. Ink-jet printing: Perfect tool for cantilever array sensor preparation for microbial growth detection. J Sens 2012. 2012:7.
-
- Cho MO, Yoon S, Kim JK. Inkjet Printing of High-Density Bacterial Arrays for Biosensor Applications. In: ASME 2010 First Global Congress on Nano Engineering for Medicine and Biology. American Society of Mechanical Engineers. 2010
-
- Srimongkon T, Mandai S, Enomae T. Application of biomaterials and inkjet printing to develop bacterial culture system. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2015. 2015:9.
-
- Kuswandi B, Wicaksono Y, Jayus, Abdullah A, Heng LY, Ahmad M, et al. Smart packaging: Sensors for monitoring of food quality and safety. Sens Instrum Food Qual Saf. 2011;5:137–46.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

