Therapeutic Targeting of Endosomal G-Protein-Coupled Receptors
- PMID: 30180973
- PMCID: PMC6508874
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.08.003
Therapeutic Targeting of Endosomal G-Protein-Coupled Receptors
Abstract
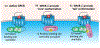
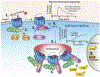
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are conventionally considered to function at the plasma membrane, where they detect extracellular ligands and activate heterotrimeric G proteins that transmit intracellular signals. Consequently, drug discovery efforts have focused on identification of agonists and antagonists of cell surface GPCRs. However, β-arrestin (ARR)-dependent desensitization and endocytosis rapidly terminate G protein signaling at the plasma membrane. Emerging evidence indicates that GPCRs can continue to signal from endosomes by G-protein- and βARR-dependent processes. By regulating the duration and location of intracellular signaling events, GPCRs in endosomes control critically important processes, including gene transcription and ion channel activity. Thus, GPCRs in endosomes, in addition to at the cell surface, have emerged as important therapeutic targets.
Keywords: compartmentalized signaling; endosomes; receptor trafficking.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beneath the surface: endosomal GPCR signaling.Trends Biochem Sci. 2024 Jun;49(6):520-531. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2024.03.006. Epub 2024 Apr 19. Trends Biochem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38643023 Review.
-
G protein-regulated endocytic trafficking of adenylyl cyclase type 9.Elife. 2020 Jun 9;9:e58039. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58039. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32515353 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Membrane Trafficking and Endosomal Signaling of G Protein-Coupled Receptors.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2018;339:93-131. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29776606 Review.
-
Neurokinin 1 receptor signaling in endosomes mediates sustained nociception and is a viable therapeutic target for prolonged pain relief.Sci Transl Med. 2017 May 31;9(392):eaal3447. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3447. Sci Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28566424 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin-converting enzyme 1 degrades neuropeptides in endosomes to control receptor recycling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jul 10;104(28):11838-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701910104. Epub 2007 Jun 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17592116 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
An Overview of VPAC Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Biological Role and Clinical Significance.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Oct 22;10:729. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00729. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31695683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholesterol-dependent endocytosis of GPCRs: implications in pathophysiology and therapeutics.Biophys Rev. 2021 Nov 12;13(6):1007-1017. doi: 10.1007/s12551-021-00878-7. eCollection 2021 Dec. Biophys Rev. 2021. PMID: 35059024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorescent ligands: Bringing light to emerging GPCR paradigms.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Mar;177(5):978-991. doi: 10.1111/bph.14953. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31877233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome: A pathophysiological manifestation of the Bloch hypothesis.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Jan 12;10:1120373. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1120373. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36714259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of polycystic kidney disease by G-protein coupled receptors and cyclic AMP signaling.Cell Signal. 2020 Aug;72:109649. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109649. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 32335259 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

