Enzyme activity and phosphate uptake in the small intestine of Sprague Dawley rats improved by supplementation of infant formula with prebiotics
- PMID: 30175258
- PMCID: PMC6116332
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aninu.2018.06.003
Enzyme activity and phosphate uptake in the small intestine of Sprague Dawley rats improved by supplementation of infant formula with prebiotics
Abstract
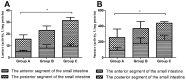
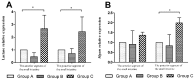
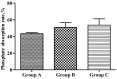
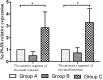
This study was to identify the effects of prebiotics supplemented in infant formula on enzyme activity and phosphate uptake in the small intestine of Sprague Dawley (SD) rats. Forty-eight healthy SD rats at 15 days old (a week before weaning) with similar weight were randomly divided into 3 groups: A (control group), B, C, with 16 rats per group. Rats in groups A, B, C were fed a standard infant formula, the standard infant formula supplemented with oligosaccharides, and the standard infant formula supplemented with polysaccharides, respectively. The feeding test was conducted for 28 d. Compared with group A, the results showed the following: 1) the activities of sucrose and lactase in the small intestine were significantly increased in SD rats of group C (P < 0.05); 2) the relative expressions of lactase gene in the anterior and posterior segments of the small intestine were significantly increased by 1.68 and 2.26 in SD rats of group C (P < 0.05), and the relative expression of Mgam gene in the posterior segment of the small intestine was significantly increased by 0.99 in SD rats of group C (P < 0.05); 3) the relative expressions of Na/Pi-IIb gene in the anterior and posterior segments of the small intestine were significantly increased by 1.85 and 2.28 in SD rats of group C (P < 0.05). These results indicate that the supplementation of infant formula with prebiotics can promote enzyme activity in the small intestine by increasing the relative expression of enzyme gene or by decreasing intestinal injury, and can increase the relative expression of Na/Pi-IIb gene. The effect of polysaccharides is better than that of oligosaccharides.
Keywords: Infant formula; Intestinal enzyme activities; Phosphate absorption; Prebiotics; Ussing chamber.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prebiotics in infant formula.Gut Microbes. 2014;5(6):681-7. doi: 10.4161/19490976.2014.972237. Gut Microbes. 2014. PMID: 25535999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on messenger RNA expression of caveolin-1, NOS, and genes regulating oxidative stress in the terminal ileum of formula-fed neonatal rats.Pediatr Res. 2010 May;67(5):526-31. doi: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181d4ff2b. Pediatr Res. 2010. PMID: 20101198
-
Quantitative analysis of intestinal bacterial populations from term infants fed formula supplemented with fructo-oligosaccharides.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012 Sep;55(3):314-20. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e3182523254. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22395187 Clinical Trial.
-
Soy-polysaccharide-supplemented soy formula enhances mucosal disaccharidase levels following massive small intestinal resection in rats.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1997 Feb;24(2):140-5. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199702000-00006. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1997. PMID: 9106099
-
Oligosaccharides in infant formula: more evidence to validate the role of prebiotics.Br J Nutr. 2015 May 14;113(9):1339-44. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515000823. Br J Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25989994 Review.
References
-
- Al-Sheraji S.H., Ismail A., Manap M.Y., Mustafa S., Yusof R.M., Hassan F.A. Prebiotics as functional foods: a review. Journal of Functional Foods. 2013;5(4):1542–1553.
-
- Biber J., Hernando N., Forster I., Murer H. Regulation of phosphate transport in proximal tubules. Pflueg Arch Eur J Physiol. 2009;458(1):39–52. - PubMed
-
- Bode L. The functional biology of human milk oligosaccharides. Early Hum Dev. 2015;91(11):619–622. - PubMed
-
- Boehm G., Stahl B. Oligosaccharides from milk. J Nutr. 2007;137(2):847S–849S. - PubMed
-
- Braegger C., Chmielewska A., Decsi T., Kolacek S., Mihatsch W., Moreno L. Supplementation of infant formula with probiotics and/or prebiotics: a systematic review and comment by the ESPGHAN committee on nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011;52(2):238–250. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

