Role of Adiponectin in Central Nervous System Disorders
- PMID: 30150999
- PMCID: PMC6087588
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/4593530
Role of Adiponectin in Central Nervous System Disorders
Abstract
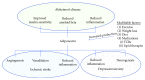
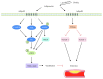
Adiponectin, the most abundant plasma adipokine, plays an important role in the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Adiponectin also possesses insulin-sensitizing, anti-inflammatory, angiogenic, and vasodilatory properties which may influence central nervous system (CNS) disorders. Although initially not thought to cross the blood-brain barrier, adiponectin enters the brain through peripheral circulation. In the brain, adiponectin signaling through its receptors, AdipoR1 and AdipoR2, directly influences important brain functions such as energy homeostasis, hippocampal neurogenesis, and synaptic plasticity. Overall, based on its central and peripheral actions, recent evidence indicates that adiponectin has neuroprotective, antiatherogenic, and antidepressant effects. However, these findings are not without controversy as human observational studies report differing correlations between plasma adiponectin levels and incidence of CNS disorders. Despite these controversies, adiponectin is gaining attention as a potential therapeutic target for diverse CNS disorders, such as stroke, Alzheimer's disease, anxiety, and depression. Evidence regarding the emerging role for adiponectin in these disorders is discussed in the current review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adiponectin receptor signalling in the brain.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;165(2):313-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01560.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21718299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adiponectin and Cognitive Decline.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 16;21(6):2010. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062010. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32188008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adiponectin as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Prostate Cancer.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(28):4170-4179. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170208123553. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28183249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
APPL1: role in adiponectin signaling and beyond.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Jan;296(1):E22-36. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90731.2008. Epub 2008 Oct 14. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 18854421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adiponectin controls the apoptosis and the expression of tight junction proteins in brain endothelial cells through AdipoR1 under beta amyloid toxicity.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Oct 12;8(10):e3102. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.491. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 29022894 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Adiponectin: Structure, Physiological Functions, Role in Diseases, and Effects of Nutrition.Nutrients. 2021 Apr 2;13(4):1180. doi: 10.3390/nu13041180. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33918360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distribution of Adiponectin Receptors in the Brain of Adult Mouse: Effect of a Single Dose of the Adiponectin Receptor Agonist, AdipoRON, on Ischemic Stroke.Brain Sci. 2022 May 23;12(5):680. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12050680. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35625066 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Peripheral Biomarkers and Reduction of Stress Response in Patients With Major Depressive Disorders vs. Panic Disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Mar 31;13:842963. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.842963. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35432030 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin receptor 1-mediated stimulation of Cav3.2 channels in trigeminal ganglion neurons induces nociceptive behaviors in mice.J Headache Pain. 2023 Aug 25;24(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01658-2. J Headache Pain. 2023. PMID: 37620777 Free PMC article.
-
The Protective Effect of Adiponectin-Transfected Endothelial Progenitor Cells on Cognitive Function in D-Galactose-Induced Aging Rats.Neural Plast. 2020 Mar 23;2020:1273198. doi: 10.1155/2020/1273198. eCollection 2020. Neural Plast. 2020. PMID: 32273888 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen M.-C., Lee C.-J., Yang C.-F., Chen Y.-C., Wang J.-H., Hsu B.-G. Low serum adiponectin level is associated with metabolic syndrome and is an independent marker of peripheral arterial stiffness in hypertensive patients. Diabetology and Metabolic Syndrome. 2017;9(1):p. 49. doi: 10.1186/s13098-017-0247-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

