Transvascular Delivery of Hydrophobically Modified siRNAs: Gene Silencing in the Rat Brain upon Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier
- PMID: 30143435
- PMCID: PMC6225091
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.08.005
Transvascular Delivery of Hydrophobically Modified siRNAs: Gene Silencing in the Rat Brain upon Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier
Abstract
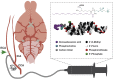
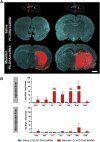
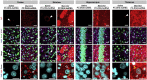
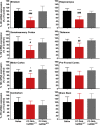
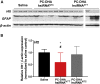
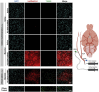
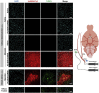
Effective transvascular delivery of therapeutic oligonucleotides to the brain presents a major hurdle to the development of gene silencing technologies for treatment of genetically defined neurological disorders. Distribution to the brain after systemic administrations is hampered by the low permeability of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and the rapid clearance kinetics of these drugs from the blood. Here we show that transient osmotic disruption of the BBB enables transvascular delivery of hydrophobically modified small interfering RNA (hsiRNA) to the rat brain. Intracarotid administration of 25% mannitol and hsiRNA conjugated to phosphocholine-docosahexanoic acid (PC-DHA) resulted in broad ipsilateral distribution of PC-DHA-hsiRNAs in the brain. PC-DHA conjugation enables hsiRNA retention in the parenchyma proximal to the brain vasculature and enabled active internalization by neurons and astrocytes. Moreover, transvascular delivery of PC-DHA-hsiRNAs effected Htt mRNA silencing in the striatum (55%), hippocampus (51%), somatosensory cortex (52%), motor cortex (37%), and thalamus (33%) 1 week after administration. Aside from mild gliosis induced by osmotic disruption of the BBB, transvascular delivery of PC-DHA-hsiRNAs was not associated with neurotoxicity. Together, these findings provide proof-of-concept that temporary disruption of the BBB is an effective strategy for the delivery of therapeutic oligonucleotides to the brain.
Keywords: RNA interference; hyperosmolar mannitol; intracarotid injection; osmotic disruption; therapeutic oligonucleotide.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
Gene Silencing in the Right Place at the Right Time.Mol Ther. 2018 Nov 7;26(11):2539-2541. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.10.005. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Mol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30366821 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of Parenchymal Retention and Efficacy of a Metabolically Stable O-Phosphocholine-N-docosahexaenoyl-l-serine siRNA Conjugate in Mouse Brain.Bioconjug Chem. 2017 Jun 21;28(6):1758-1766. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.7b00226. Epub 2017 May 10. Bioconjug Chem. 2017. PMID: 28462988 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-mediated Delivery of Hydrophobically Modified siRNA for Huntingtin mRNA Silencing.Mol Ther. 2016 Oct;24(10):1836-1847. doi: 10.1038/mt.2016.126. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Mol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27506293 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of pentobarbital on blood-brain barrier disruption caused by intracarotid injection of hyperosmolar mannitol in rats.Anesth Analg. 1998 Jun;86(6):1230-5. doi: 10.1097/00000539-199806000-00018. Anesth Analg. 1998. PMID: 9620510
-
Outwitting the blood-brain barrier for therapeutic purposes: osmotic opening and other means.Neurosurgery. 1998 May;42(5):1083-99; discussion 1099-100. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199805000-00082. Neurosurgery. 1998. PMID: 9588554 Review.
-
Hyperosmolar blood-brain barrier opening using intra-arterial injection of hyperosmotic mannitol in mice under real-time MRI guidance.Nat Protoc. 2022 Jan;17(1):76-94. doi: 10.1038/s41596-021-00634-x. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Nat Protoc. 2022. PMID: 34903870 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of complexity in non-viral oligonucleotide delivery systems: from gymnotic delivery through bioconjugates to biomimetic nanoparticles.RNA Biol. 2022 Jan;19(1):1256-1275. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2022.2147278. RNA Biol. 2022. PMID: 36411594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrathecal Delivery of Therapeutic Oligonucleotides for Potent Modulation of Gene Expression in the Central Nervous System.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2434:345-353. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2010-6_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35213030 Free PMC article.
-
Self-delivering, chemically modified CRISPR RNAs for AAV co-delivery and genome editing in vivo.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 25;52(2):977-997. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1125. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38033325 Free PMC article.
-
Potentially Detrimental Effects of Hyperosmolality in Patients Treated for Traumatic Brain Injury.J Clin Med. 2021 Sep 14;10(18):4141. doi: 10.3390/jcm10184141. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34575255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulating the Blood-Brain Barrier: A Comprehensive Review.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Nov 22;13(11):1980. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13111980. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34834395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pasi K.J., Rangarajan S., Georgiev P., Mant T., Creagh M.D., Lissitchkov T., Bevan D., Austin S., Hay C.R., Hegemann I. Targeting of antithrombin in hemophilia A or B with RNAi therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017;377:819–828. - PubMed
-
- Ray K.K., Landmesser U., Leiter L.A., Kallend D., Dufour R., Karakas M., Hall T., Troquay R.P., Turner T., Visseren F.L. Inclisiran in patients at high cardiovascular risk with elevated LDL cholesterol. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017;376:1430–1440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

